Overview
Diagnosis
Toe walking can often be observed during a physical exam. In some cases, your healthcare professional may perform a gait analysis or an electromyography (EMG) exam.
During EMG, a thin needle with an electrode is inserted into a leg muscle. The electrode measures electrical activity in the affected nerve or muscle.
If a condition such as cerebral palsy or autism spectrum disorder is suspected, your child may also undergo a neurological exam or testing for developmental delays.
Treatment
If toe walking is purely a habit, treatment is usually not needed, as your child is likely to outgrow it. Healthcare professionals may simply monitor your child’s gait during office visits.
If a physical issue contributes to toe walking, treatment options may include:
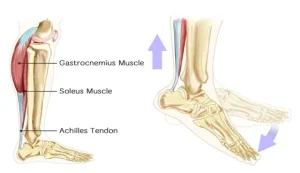
• Physical therapy: Gentle stretching of the leg and foot muscles can improve gait
• Leg braces or splints: These devices may help promote a normal walking pattern
• Serial casting: A series of below-the-knee casts may progressively improve the ability to bring the toes toward the shin if other methods are not effective
• OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) injections: Sometimes used in the calf muscles to help improve gait
• Surgery: Recommended if conservative treatments fail, to lengthen muscles or tendons at the back of the lower leg
When toe walking is related to cerebral palsy, autism spectrum disorder, or other underlying conditions, treatment will also focus on managing the primary condition.
Advertisement