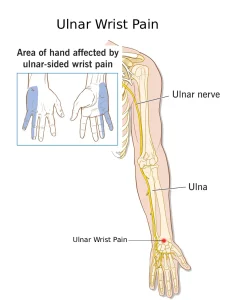
Overview
Diagnosis
To diagnose the cause of ulnar wrist pain, a healthcare professional will begin with a physical examination. During the exam, your wrist and hand may be moved into different positions to identify the source of pain. The doctor will also assess your range of motion and grip strength to determine the extent of the problem.
Imaging tests may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis or detect underlying issues.
Common imaging tests include:
-
X-ray: The most common test for wrist pain. It uses a small amount of radiation to identify fractures or signs of osteoarthritis.
-
CT scan: Provides detailed images of wrist bones and can detect fractures that may not appear on X-rays.
-
MRI: Uses radio waves and magnetic fields to create detailed images of bones, tendons, and ligaments. For wrist evaluation, a smaller MRI device may be used instead of a full-body scanner.
-
Ultrasound: A simple and noninvasive test that helps visualize tendons, ligaments, and cysts.
Treatment
Treatment for ulnar wrist pain depends on the cause and severity of the condition. It may involve medication, physical therapy, immobilization, or surgery.
Medicines
Over-the-counter pain relievers can help reduce discomfort and inflammation.
-
Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB)
-
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
For more severe pain, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy plays a key role in recovery. Exercises help strengthen tendons and ligaments while improving flexibility and function. A physical therapist can also teach ways to adjust daily activities to reduce strain on the wrist.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend immobilizing the wrist with a cast, brace, or splint to allow proper healing.
Surgery
If conservative treatments do not relieve symptoms, surgery may be necessary. Minimally invasive surgical methods are often used to repair damaged structures in the wrist. These procedures typically result in less pain, faster recovery, shorter hospital stays, and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery.
Advertisement