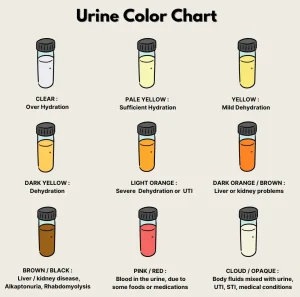
Overview
Diagnosis
Your healthcare provider will begin by reviewing your medical history and performing a physical examination. To determine the cause of changes in urine color, you may need one or more diagnostic tests.
Common tests include:
-
Urinalysis: This test examines a urine sample for signs of kidney or urinary tract issues. It also checks for the presence of bacteria that can cause infections or illness.
-
Blood tests: These measure levels of waste products that accumulate in the bloodstream when kidney function is impaired. Blood tests can also reveal liver problems, diabetes, or other underlying health conditions that may contribute to changes in urine color.
These evaluations help identify whether the discoloration is due to a temporary issue, such as diet or medication, or a more serious condition affecting the kidneys, liver, or urinary tract.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the change in urine color. In many cases, no specific treatment is needed if the cause is harmless, such as certain foods or vitamins. If a medical condition is responsible, your healthcare provider will recommend appropriate treatment to address that condition and restore normal urine color.
Advertisement