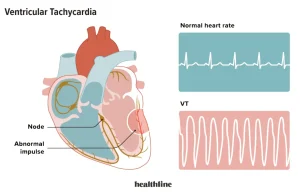
Overview
Diagnosis
A thorough physical exam, medical history, and various tests are required to diagnose ventricular tachycardia. In some cases, this condition may require emergency care and is diagnosed at a hospital. When possible, a healthcare professional may ask you or your family questions about symptoms, lifestyle habits, and medical history.
Tests
Tests are performed to check the heart and confirm a diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT). The results also help identify if another health problem is causing the irregular heartbeat.
Common tests include:
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) – The most common test used to diagnose tachycardia. It records the heart’s electrical activity through sensors attached to the chest, arms, and legs.
-
Holter monitor – A small portable ECG device worn for a day or more to record heart activity during normal daily routines. Some smartwatches also provide ECG monitoring.
-
Event monitor – A portable ECG worn for up to 30 days. You press a button when symptoms occur to record the heart’s activity.
-
Implantable loop recorder – A device placed just under the skin of the chest that continuously records the heart’s rhythm for up to three years.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests help check the structure and function of the heart. These may include:
-
Chest X-ray – Shows the size and condition of the heart and lungs.
-
Echocardiogram – An ultrasound that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart, showing areas of poor blood flow or valve issues.
-
Exercise stress test – Monitors how the heart responds during exercise, such as walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike.
-
Cardiac MRI – Produces detailed images of the heart and blood flow, helping identify causes of V-tach or ventricular fibrillation.
-
Cardiac CT scan – Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the heart to look for structural problems or blockages.
-
Coronary angiogram – Uses dye and special X-rays to show the inside of coronary arteries and detect narrowing or blockages.
Additional Diagnostic Tests
Other tests may be done to confirm the diagnosis and understand how V-tach affects overall health:
-
Electrophysiological (EP) study – Maps how electrical signals move through the heart to find where abnormal signals originate. It involves inserting thin, flexible tubes into blood vessels leading to the heart.
-
Tilt table test – Helps determine how tachycardia leads to fainting. You are strapped to a table that tilts slowly from lying down to standing, while heart rate and blood pressure are monitored.
Treatment
Ventricular tachycardia that lasts longer than 30 seconds, known as sustained V-tach, requires emergency medical care. Without treatment, it can lead to sudden cardiac death. The main goals of treatment are to slow the rapid heartbeat and prevent future episodes. Treatment may involve medications, procedures, or devices that control or reset heart rhythm, as well as surgery when necessary.
Medications
Medicines are used to slow the heart rate and stabilize rhythm. Beta blockers are commonly prescribed, and sometimes a combination of medications is needed. The type of medicine depends on individual health conditions and risk factors.
Surgery or Procedures
Certain procedures or surgeries may be necessary to manage or prevent episodes of tachycardia:
-
Cardioversion – Delivers controlled electrical shocks to reset the heart rhythm, often used in emergency situations.
-
Catheter ablation – Uses heat or cold energy to destroy small areas of heart tissue causing abnormal electrical signals.
-
Open-heart surgery – Performed when other treatments fail or when surgery is already needed for another heart condition.
Heart Devices
Some people require devices to monitor or regulate heart rhythm:
-
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) – Placed under the skin near the collarbone, it continuously monitors heart rhythm and delivers shocks to correct life-threatening arrhythmias.
-
Pacemaker – Sends electrical impulses to correct slow or irregular heartbeats when no reversible cause is identified.
These treatments and diagnostic approaches are designed to restore and maintain a healthy heart rhythm, improving overall heart function and preventing serious complications.
Advertisement