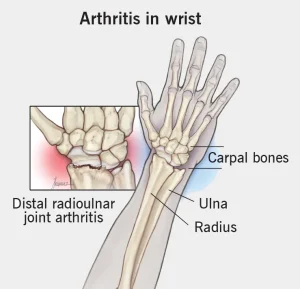
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosing wrist pain involves understanding the cause, which can range from sudden injuries to chronic conditions like arthritis or carpal tunnel syndrome. A healthcare professional begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination.
Diagnostic steps may include:
-
Physical examination: The healthcare provider checks for swelling, tenderness, range of motion, and visible deformities in the wrist.
-
Medical history: Questions about recent injuries, repetitive activities, or preexisting conditions help identify possible causes.
-
Imaging tests:
-
X-rays detect fractures or joint damage.
-
MRI or CT scans provide detailed images of soft tissues, including ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
-
Ultrasound helps assess tendon movement or inflammation.
-
-
Nerve studies: If carpal tunnel syndrome is suspected, an electromyogram (EMG) or nerve conduction study may be used to measure nerve function.
-
Arthroscopy: In rare cases, a small camera may be inserted into the joint to view internal structures and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for wrist pain depends on the underlying cause, severity, and duration of symptoms. The main goals are to reduce pain, restore function, and prevent further injury.
Common treatment options include:
-
Rest and immobilization:
-
Wearing a splint or brace can support the wrist and limit movement while it heals.
-
Avoiding repetitive movements and giving the wrist time to rest helps reduce strain.
-
-
Medications:
-
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation.
-
Corticosteroid injections may be used for severe inflammation or chronic conditions like arthritis.
-
-
Physical therapy:
-
Exercises that strengthen wrist muscles and improve flexibility can aid recovery and prevent recurrence.
-
Therapists may also teach ergonomic techniques to protect the wrist during daily activities.
-
-
Surgical treatments:
-
Surgery may be needed for severe fractures, torn ligaments, or nerve compression (such as in carpal tunnel release).
-
Arthroscopic surgery allows precise repairs with smaller incisions and quicker recovery.
-
-
Home care and lifestyle changes:
-
Apply ice packs for 15–20 minutes several times a day to reduce swelling.
-
Maintain a healthy weight and posture to reduce stress on wrist joints.
-
Use ergonomic keyboards or wrist supports if pain is related to repetitive tasks.
-
Early diagnosis and appropriate management help prevent long-term wrist problems and restore normal function efficiently.
Advertisement