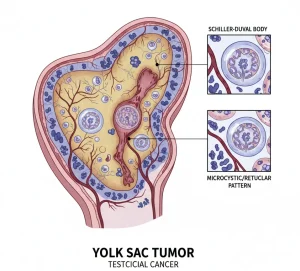
Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a yolk sac tumor involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and laboratory studies. Since these tumors are rare and aggressive, early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment.
Healthcare professionals typically begin with a physical examination and review of symptoms such as abdominal swelling, pain, or the presence of a lump in the testicles or ovaries.
Common diagnostic tests include:
-
Blood tests: Elevated levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the blood are a key marker for yolk sac tumors. Measuring AFP helps in both diagnosis and monitoring response to treatment.
-
Imaging studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans help locate the tumor and assess whether it has spread to other organs.
-
Biopsy: A tissue sample from the tumor is examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis. The biopsy can identify the characteristic features of yolk sac tumors and rule out other germ cell tumors.
If the tumor is found in the testicles, an orchiectomy (surgical removal of the testicle) may be performed both for diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment
Treatment for yolk sac tumors depends on factors such as the tumor’s location, size, and whether it has spread. Because these tumors grow quickly, prompt treatment is crucial.
Main treatment options include:
-
Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is often the first step. In males, this may involve removing the affected testicle (radical inguinal orchiectomy). For females, surgery may involve removal of the affected ovary while trying to preserve fertility if possible.
-
Chemotherapy: This is the most effective treatment for yolk sac tumors. Common chemotherapy drugs include bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin (the BEP regimen). Chemotherapy helps destroy any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
-
Radiation therapy: Rarely used for yolk sac tumors, but it may be considered in certain cases when surgery or chemotherapy alone isn’t sufficient.
-
Follow-up care: Regular follow-ups are essential after treatment. AFP levels are monitored to detect any signs of recurrence early. Imaging tests may also be repeated periodically.
Outlook
With modern chemotherapy, the prognosis for yolk sac tumors has significantly improved, especially when diagnosed early. Children tend to have better outcomes than adults. However, continuous monitoring is important, as these tumors can recur.
Early diagnosis, effective surgical removal, and combination chemotherapy remain the cornerstone of successful treatment and long-term recovery.
Advertisement