Overview
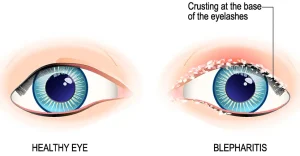
Blepharitis is a common eye condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelids, particularly along the edges where the eyelashes grow. It often occurs when the tiny oil glands near the base of the eyelashes become clogged or irritated. Blepharitis is usually a chronic condition that can flare up periodically, but it is not contagious.
Although blepharitis can be uncomfortable and persistent, it rarely causes serious damage to vision when properly managed. Long-term eyelid hygiene plays a key role in controlling symptoms.
Symptoms
Symptoms of blepharitis may affect one or both eyes and can vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
-
Red, swollen, or irritated eyelids
-
Itching or burning sensation in the eyes
-
Crusty or flaky debris at the base of the eyelashes
-
Watery or dry eyes
-
Gritty or foreign body sensation in the eyes
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Blurred vision that improves with blinking
Symptoms are often worse in the morning.
Causes
Blepharitis develops due to irritation or inflammation of the eyelid margins. It is commonly linked to problems with the oil-producing glands in the eyelids.
Common causes include:
-
Blocked or malfunctioning oil glands
-
Bacterial overgrowth on the eyelids
-
Skin conditions such as dandruff or rosacea
-
Allergic reactions
-
Infestation of eyelash mites
In many cases, more than one factor contributes to the condition.
Risk factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing blepharitis, including:
-
History of skin conditions like dandruff or rosacea
-
Poor eyelid hygiene
-
Oily skin
-
Use of eye makeup, especially if not removed properly
-
Wearing contact lenses
Blepharitis can occur at any age and often recurs over time.
Complications
If not properly managed, blepharitis can lead to complications such as:
-
Recurrent styes or chalazia
-
Chronic dry eye symptoms
-
Eyelash problems, including loss or abnormal growth
-
Inflammation of the cornea
-
Increased eye discomfort or irritation
Most complications can be prevented with consistent eyelid care.
Prevention
While blepharitis cannot always be completely prevented, good eye hygiene can reduce flare-ups and severity. Preventive measures include:
-
Cleaning eyelids regularly with warm compresses
-
Gently washing eyelids to remove crusts and oil buildup
-
Removing eye makeup thoroughly before sleeping
-
Avoiding sharing eye cosmetics
-
Managing underlying skin conditions
Maintaining proper eyelid hygiene is the most effective way to control blepharitis and prevent recurrence.
Advertisement