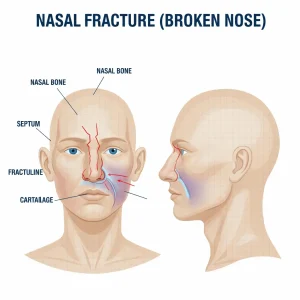
Overview
A broken nose, also called a nasal fracture, is a crack or break in the bones or cartilage of the nose. It is one of the most common facial injuries and often occurs after direct impact to the face. A broken nose can range from a small crack to a displaced fracture that alters the shape of the nose. Prompt medical evaluation is important to assess damage, manage symptoms, and prevent breathing or cosmetic problems.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a broken nose usually appear immediately after injury and may include:
-
Pain and tenderness around the nose
-
Swelling of the nose and surrounding facial area
-
Bruising under the eyes or around the nose
-
Nosebleeds
-
Difficulty breathing through the nose
-
A crooked or misshapen appearance
In some cases, a cracking or popping sound may be heard at the time of injury.
Causes
A broken nose is most often caused by blunt force trauma to the face. Common causes include:
-
Sports injuries, especially in contact sports
-
Physical altercations or assaults
-
Falls, particularly face-first falls
-
Motor vehicle or bicycle accidents
-
Accidental impact with hard objects
Risk factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of a broken nose:
-
Participation in contact or high-risk sports
-
Not wearing protective facial gear
-
Poor balance or coordination
-
Alcohol use, which may increase fall risk
-
Previous nasal injuries or fractures
Complications
Most broken noses heal well with appropriate treatment, but complications can occur:
-
Persistent nasal blockage or breathing difficulties
-
Septal hematoma, a collection of blood inside the nose
-
Infection within the nasal tissues
-
Changes in the shape or appearance of the nose
-
Chronic nosebleeds
Untreated complications may lead to long-term functional or cosmetic issues.
Prevention
Not all broken noses can be prevented, but the following steps may reduce risk:
-
Wearing protective face masks during sports
-
Using seat belts and appropriate safety equipment
-
Taking precautions to prevent falls
-
Avoiding physical confrontations
-
Following safety guidelines at work and during recreational activities
Early assessment and proper care can help ensure correct healing and reduce the risk of lasting complications.
Advertisement