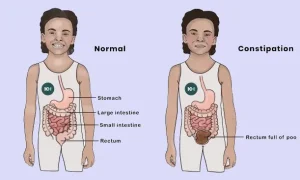
Overview
Constipation in children is a common digestive problem in which a child has infrequent bowel movements, hard stools, or difficulty passing stools. It can occur at any age, from infancy through adolescence, and is often temporary. In many cases, childhood constipation is related to diet, toilet habits, or routine changes rather than a serious medical condition.
Symptoms
Symptoms of constipation in children may vary depending on age and severity. Common symptoms include:
-
Fewer bowel movements than usual for the child’s age
-
Hard, dry, or large stools
-
Pain or straining during bowel movements
-
Abdominal pain or bloating
-
Stool withholding behaviors, such as crossing legs or hiding
-
Soiling or stool leakage in underwear
-
Poor appetite or irritability
Causes
Constipation in children often occurs when stool moves slowly through the intestines. Common causes include low fiber intake, inadequate fluid consumption, and toilet training difficulties. Emotional stress, changes in routine, illness, or reluctance to use unfamiliar bathrooms can also contribute. In infants, changes in feeding may play a role.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of constipation in children:
-
Diet low in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
-
Limited water intake
-
Inadequate physical activity
-
Stressful events such as starting school or travel
-
History of painful bowel movements
-
Delayed or difficult toilet training
Complications
If not properly managed, constipation in children can lead to complications:
-
Anal fissures causing pain and bleeding
-
Stool impaction
-
Encopresis, or involuntary stool leakage
-
Abdominal discomfort and behavioral issues
-
Fear or avoidance of bowel movements
-
Reduced quality of life for the child
Prevention
Many cases of constipation in children can be prevented with healthy habits:
-
Providing a balanced, fiber-rich diet appropriate for age
-
Encouraging regular fluid intake
-
Promoting daily physical activity
-
Establishing regular toilet routines, especially after meals
-
Offering positive reinforcement during toilet training
-
Addressing constipation early to prevent recurrence
Advertisement