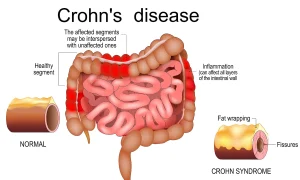
Overview
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes long-term inflammation of the digestive tract. It can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus, but most commonly involves the end of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. Crohn’s disease is a lifelong condition characterized by periods of flare-ups and remission. Ongoing inflammation can lead to digestive symptoms and complications that affect overall health and quality of life.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Crohn’s disease vary widely depending on the location and severity of inflammation.
Common symptoms include:
-
Persistent diarrhea
-
Abdominal pain and cramping
-
Blood in the stool
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Unintended weight loss
-
Reduced appetite
-
Fever during active inflammation
-
Mouth sores
In children, delayed growth or puberty may occur due to poor nutrient absorption.
Causes
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from an abnormal immune response.
Contributing factors include:
-
Immune system attacking the digestive tract
-
Genetic susceptibility
-
Altered gut bacteria
-
Environmental factors such as smoking
-
Past infections that may trigger immune dysfunction
Crohn’s disease is not caused by diet alone, but certain foods can worsen symptoms during flare-ups.
Risk factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing Crohn’s disease.
Risk factors include:
-
Family history of inflammatory bowel disease
-
Smoking, which increases disease severity
-
Onset commonly in adolescence or early adulthood
-
Use of certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
-
Living in urban or industrialized regions
Both men and women are affected equally.
Complications
Without proper management, Crohn’s disease can lead to serious complications.
Possible complications include:
-
Intestinal strictures causing bowel obstruction
-
Fistulas between the intestine and other organs
-
Abscesses and infections
-
Malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies
-
Increased risk of colon cancer
-
Delayed growth and development in children
Early and consistent treatment helps reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention
There is no proven way to prevent Crohn’s disease, but certain steps may help reduce flare-ups and maintain remission.
Preventive strategies include:
-
Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke
-
Following a personalized nutrition plan
-
Managing stress effectively
-
Taking prescribed medications as directed
-
Regular medical follow-up and screening
Lifestyle adjustments combined with medical care play an important role in long-term disease control.
Advertisement