Overview
Cushing syndrome is a hormonal disorder caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Cortisol plays an important role in regulating metabolism, immune response, and the body’s reaction to stress. When cortisol levels remain elevated for long periods, it can disrupt multiple body systems. Cushing syndrome may develop due to the body producing too much cortisol or from long-term use of corticosteroid medications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Cushing syndrome often develop gradually and may vary in severity from person to person.
Common symptoms include:
-
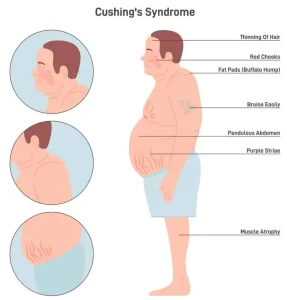
Weight gain, especially around the abdomen, face, and upper back
-
Rounded face appearance
-
Thinning skin that bruises easily
-
Purple or pink stretch marks on the abdomen, thighs, or arms
-
Muscle weakness, particularly in the upper arms and thighs
-
Fatigue and low energy levels
-
High blood pressure
-
Mood changes such as depression, anxiety, or irritability
-
Irregular menstrual periods or excess facial hair in women
-
Decreased libido or fertility issues
Children may experience slowed growth with weight gain.
Causes
Cushing syndrome occurs when cortisol levels are abnormally high for an extended time.
Possible causes include:
-
Long-term use of corticosteroid medications such as prednisone
-
Tumors of the pituitary gland producing excess adrenocorticotropic hormone
-
Adrenal gland tumors producing excess cortisol
-
Tumors elsewhere in the body producing adrenocorticotropic hormone
-
Rare genetic conditions affecting hormone regulation
The cause may be endogenous or related to medication use.
Risk factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing Cushing syndrome.
Risk factors include:
-
Prolonged or high-dose corticosteroid therapy
-
Pituitary or adrenal tumors
-
Family history of endocrine disorders
-
Conditions requiring long-term steroid treatment, such as asthma or autoimmune diseases
-
Female sex, as the condition is more common in women
Not all individuals with these risk factors will develop the syndrome.
Complications
If untreated, Cushing syndrome can lead to serious health complications.
Possible complications include:
-
Type 2 diabetes
-
Osteoporosis and increased fracture risk
-
High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease
-
Increased susceptibility to infections
-
Muscle wasting and weakness
-
Blood clots
-
Depression and cognitive difficulties
Early diagnosis and treatment help reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Prevention
Not all cases of Cushing syndrome can be prevented, but certain measures can reduce risk, especially for medication-related cases.
Preventive strategies include:
-
Using corticosteroid medications only as prescribed
-
Regular medical monitoring during long-term steroid therapy
-
Avoiding abrupt discontinuation of steroid medications without medical guidance
-
Prompt evaluation of unexplained weight gain and hormonal symptoms
-
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers for endocrine conditions
Careful medication management and early medical attention are key to preventing complications associated with Cushing syndrome.
Advertisement