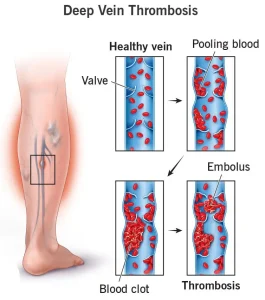
Overview
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition in which a blood clot forms in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs. The clot can partially or completely block blood flow, leading to pain and swelling. DVT is a serious condition because a clot can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. Early recognition and treatment are essential to prevent complications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of DVT may vary and sometimes develop gradually:
-
Swelling in one leg or arm
-
Pain or tenderness, often starting in the calf
-
Warmth over the affected area
-
Red or discolored skin
-
Cramping or aching sensation that may worsen with standing or walking
-
In some cases, no noticeable symptoms
Causes
DVT occurs when blood flow slows or becomes abnormal, leading to clot formation:
-
Prolonged immobility, such as during long travel or bed rest
-
Injury or trauma to a vein
-
Surgery, especially orthopedic or abdominal procedures
-
Increased blood clotting tendency
-
Compression of veins due to tumors or swelling
-
Certain medical conditions affecting circulation
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis:
-
Prolonged sitting or immobility
-
Recent surgery or hospitalization
-
Increasing age
-
Obesity
-
Pregnancy and the postpartum period
-
Smoking
-
Cancer or cancer treatment
-
Use of hormone therapy or oral contraceptives
-
Personal or family history of blood clots
Complications
If not treated promptly, DVT can lead to serious complications:
-
Pulmonary embolism
-
Chronic leg pain and swelling
-
Post-thrombotic syndrome
-
Skin ulcers due to poor circulation
-
Reduced mobility and quality of life
-
Recurrent blood clots
Prevention
Preventive measures help reduce the risk of DVT, especially in high-risk individuals:
-
Staying physically active and avoiding prolonged immobility
-
Moving legs frequently during long travel
-
Maintaining a healthy body weight
-
Quitting smoking
-
Using compression stockings when recommended
-
Following medical advice after surgery or hospitalization
-
Staying well hydrated
Advertisement