Overview
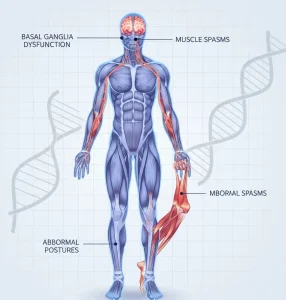
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that cause repetitive movements, twisting, or abnormal postures. These muscle contractions can affect one part of the body or multiple areas and may be sustained or intermittent. Dystonia can occur at any age and varies widely in severity, from mild and occasional symptoms to disabling muscle spasms.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the type of dystonia and the muscles involved:
-
Involuntary muscle contractions
-
Twisting or repetitive movements
-
Abnormal postures of the neck, limbs, or trunk
-
Muscle cramps or spasms
-
Tremors associated with abnormal movements
-
Pain or discomfort due to sustained muscle contraction
-
Symptoms that worsen with stress, fatigue, or activity
-
Difficulty with speech, writing, or walking in some cases
Causes
Dystonia occurs due to abnormal functioning of brain regions that control movement:
-
Genetic mutations affecting motor control
-
Dysfunction of the basal ganglia
-
Brain injury or trauma
-
Stroke
-
Infections affecting the nervous system
-
Exposure to certain medications or toxins
-
Neurodegenerative disorders
-
Unknown causes in idiopathic cases
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing dystonia:
-
Family history of dystonia or movement disorders
-
Early childhood neurological injury
-
Use of certain medications, especially long-term
-
Central nervous system infections
-
Brain trauma or stroke
-
Presence of other neurological conditions
Complications
If dystonia is severe or untreated, it may lead to:
-
Chronic pain
-
Permanent muscle contractures
-
Joint deformities
-
Difficulty performing daily activities
-
Speech or swallowing difficulties
-
Emotional distress or depression
-
Reduced quality of life
-
Social and occupational limitations
Prevention
Not all cases of dystonia can be prevented, but some strategies may reduce risk or progression:
-
Early diagnosis and neurological evaluation
-
Proper use and monitoring of medications
-
Prompt treatment of brain injuries or infections
-
Genetic counseling for inherited forms
-
Stress management techniques
-
Regular medical follow-up for symptom control
Advertisement