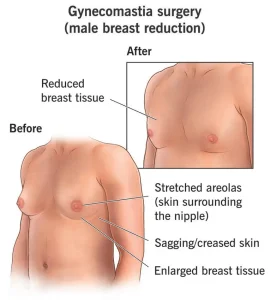
Overview
Enlarged breasts in men, medically known as gynecomastia, is a condition characterized by the benign enlargement of male breast tissue. It occurs due to an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts and may develop at different stages of life, including infancy, adolescence, and older adulthood. While it is not usually a serious condition, it can cause physical discomfort and emotional distress.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gynecomastia can vary in severity and may develop gradually. Common symptoms include:
-
Swelling or enlargement of breast tissue in one or both breasts
-
Breast tenderness or pain
-
Sensitivity around the nipple area
-
A firm or rubbery mass beneath the nipple
-
In rare cases, nipple discharge
Breast enlargement that is hard, uneven, or associated with skin changes should be evaluated to rule out other conditions.
Causes
Gynecomastia develops when estrogen levels increase or testosterone levels decrease, leading to breast tissue growth. Common causes include:
-
Natural hormonal changes during puberty or aging
-
Use of certain medications such as steroids, anti-androgens, or antidepressants
-
Chronic health conditions affecting the liver, kidneys, or thyroid
-
Obesity, which increases estrogen production
-
Use of alcohol, recreational drugs, or anabolic steroids
-
Hormone-producing tumors, though rare
Often, no single cause is identified, especially in adolescents and older men.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing gynecomastia:
-
Puberty-related hormonal fluctuations
-
Aging-related decline in testosterone
-
Obesity and excess body fat
-
Long-term use of specific medications
-
Chronic illnesses such as liver disease or kidney failure
-
Substance use, including alcohol and marijuana
The presence of risk factors does not always result in gynecomastia but increases vulnerability.
Complications
Gynecomastia is usually not physically harmful, but it can lead to certain complications:
-
Emotional distress, embarrassment, or low self-esteem
-
Social anxiety or body image concerns
-
Breast pain or tenderness affecting daily comfort
-
Persistence of breast enlargement if the underlying cause is not addressed
Early evaluation can help identify reversible causes and prevent long-term issues.
Prevention
Gynecomastia cannot always be prevented, but some measures may help reduce the risk:
-
Maintaining a healthy body weight
-
Avoiding misuse of steroids and recreational drugs
-
Limiting alcohol consumption
-
Reviewing medications with a healthcare provider
-
Managing chronic health conditions effectively
Prompt medical consultation for hormonal or physical changes helps ensure appropriate management and reassurance.
Advertisement