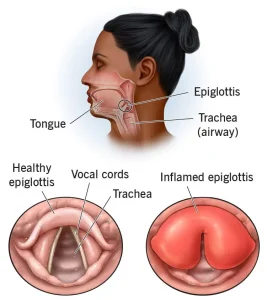
Overview
Epiglottitis is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition characterized by inflammation and swelling of the epiglottis, the flap of tissue that covers the windpipe during swallowing. When the epiglottis becomes swollen, it can block airflow to the lungs, making breathing difficult. Epiglottitis can affect both children and adults and requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms
Symptoms of epiglottitis usually develop rapidly and can worsen quickly. Common symptoms include:
-
Severe sore throat
-
Difficulty swallowing
-
Drooling due to inability to swallow saliva
-
Hoarse or muffled voice
-
High fever
-
Painful swallowing
-
Breathing difficulty or noisy breathing
-
Sitting leaning forward to ease breathing
Sudden breathing problems are a medical emergency and require urgent care.
Causes
Epiglottitis is most commonly caused by infections, but other factors may also contribute. Common causes include:
-
Bacterial infections, especially Haemophilus influenzae type b
-
Viral or fungal infections
-
Injury to the throat from burns or foreign objects
-
Inhalation of hot liquids, smoke, or chemicals
-
Trauma to the neck or throat area
Vaccination has significantly reduced infection-related cases in children.
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing epiglottitis:
-
Lack of childhood vaccination
-
Weakened immune system
-
Chronic medical conditions
-
Exposure to respiratory infections
-
Smoking or inhalation of harmful substances
Both children and adults with these risk factors are more susceptible.
Complications
If not treated promptly, epiglottitis can lead to severe complications:
-
Complete airway obstruction
-
Respiratory failure
-
Spread of infection to surrounding tissues
-
Sepsis in severe bacterial infections
-
Death if airway blockage is not managed quickly
Early emergency treatment greatly reduces the risk of complications.
Prevention
Epiglottitis can often be prevented by reducing infection risk and protecting the airway:
-
Ensuring routine childhood vaccinations are up to date
-
Practicing good hygiene to prevent respiratory infections
-
Avoiding smoking and inhalation of toxic fumes
-
Seeking prompt medical care for severe throat pain or breathing difficulty
-
Managing chronic illnesses that weaken the immune system
Awareness of early symptoms and immediate medical intervention are critical in preventing life-threatening outcomes associated with epiglottitis.
Advertisement