Overview
H1N1 flu, commonly known as swine flu, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by the influenza A (H1N1) virus. It spreads from person to person in a manner similar to seasonal influenza, primarily through respiratory droplets released when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. While many cases are mild, H1N1 flu can cause severe illness, especially in high-risk individuals, and may require hospitalization.
Symptoms
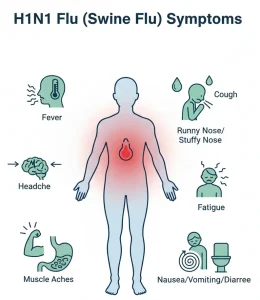
Symptoms of H1N1 flu are similar to those of seasonal influenza and usually appear suddenly. Common symptoms include:
-
Fever or chills
-
Cough
-
Sore throat
-
Runny or stuffy nose
-
Body aches and muscle pain
-
Headache
-
Fatigue or weakness
-
Shortness of breath
-
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, more common in children
Causes
H1N1 flu is caused by infection with the influenza A (H1N1) virus. The virus enters the body through the nose, mouth, or eyes and infects the respiratory tract. It spreads easily through close contact with infected individuals or by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the face.
Risk Factors
Certain groups are at higher risk of developing severe illness from H1N1 flu, including:
-
Young children
-
Older adults
-
Pregnant women
-
Individuals with chronic medical conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or heart disease
-
People with weakened immune systems
-
Obesity
Complications
Although many people recover fully, H1N1 flu can lead to serious complications, particularly in high-risk individuals. Possible complications include:
-
Pneumonia
-
Worsening of chronic medical conditions
-
Respiratory failure
-
Ear or sinus infections
-
Dehydration
-
Death in severe cases
Prevention
H1N1 flu can often be prevented through vaccination and good hygiene practices. Preventive measures include:
-
Receiving the annual influenza vaccine
-
Washing hands frequently with soap and water
-
Using alcohol-based hand sanitizers when handwashing is not possible
-
Covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
-
Avoiding close contact with people who are ill
-
Staying home when sick to prevent spreading the virus
Early medical care and preventive measures play an important role in reducing the severity and spread of H1N1 flu.
Advertisement