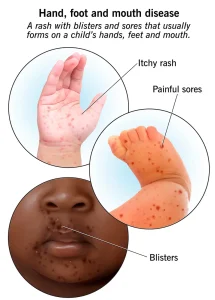
Overview
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a common viral illness that mainly affects infants and young children, though adults can also become infected. It is most often caused by enteroviruses, particularly coxsackievirus. The condition is usually mild and self-limiting, but it is highly contagious and spreads easily in childcare settings, schools, and households.
Symptoms
Symptoms typically appear 3 to 6 days after exposure and may begin with mild flu-like signs. Common symptoms include:
-
Fever
-
Sore throat
-
Reduced appetite
-
General feeling of being unwell
-
Painful sores or blisters in the mouth
-
Red rash or small blisters on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, or buttocks
-
Irritability in infants and young children
Causes
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is caused by viral infection, most commonly coxsackievirus A16 or enterovirus 71. The virus spreads through close contact with infected individuals, including:
-
Respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing
-
Contact with fluid from blisters
-
Contact with stool from an infected person
-
Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of hand-foot-and-mouth disease include:
-
Young age, especially children under 5 years
-
Attendance at daycare or school
-
Close contact with infected individuals
-
Poor hand hygiene
Complications
Most cases resolve without complications, but in rare situations, hand-foot-and-mouth disease can lead to:
-
Dehydration due to painful mouth sores
-
Viral meningitis
-
Encephalitis
-
Nail shedding several weeks after infection
-
Severe illness in rare cases involving certain virus strains
Prevention
Preventing hand-foot-and-mouth disease focuses on good hygiene and reducing virus spread:
-
Frequent handwashing with soap and water
-
Cleaning and disinfecting commonly touched surfaces
-
Avoiding close contact with infected individuals
-
Keeping children home from school or daycare during the contagious period
-
Teaching children proper cough and sneeze etiquette
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease usually resolves within 7 to 10 days, and supportive care helps relieve symptoms and promote recovery.
Advertisement