Overview
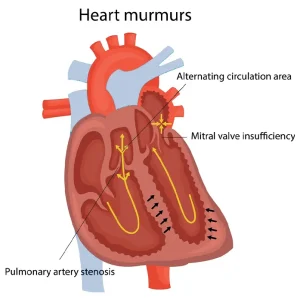
A heart murmur is an unusual sound heard during a heartbeat, often described as a whooshing or swishing noise. It is caused by turbulent blood flow within the heart or nearby blood vessels. Heart murmurs are usually detected during a physical examination using a stethoscope.
Heart murmurs can be harmless, known as innocent or functional murmurs, and may occur in healthy individuals, especially children, pregnant women, or people with fever or anemia. Other murmurs are abnormal and may indicate an underlying heart condition that affects the heart valves or structure. Whether a murmur is serious depends on its cause and associated symptoms.
Symptoms
Many people with heart murmurs have no symptoms, especially if the murmur is innocent. When symptoms do occur, they are usually related to an underlying heart problem rather than the murmur itself.
Possible symptoms include:
-
Shortness of breath, especially during activity
-
Chest pain
-
Fatigue or weakness
-
Dizziness or fainting
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
-
Swelling in the ankles, feet, or abdomen
-
Bluish discoloration of lips or fingertips in severe cases
-
Poor growth or feeding difficulties in infants
Symptoms may worsen over time if the underlying condition progresses.
Causes
Heart murmurs are caused by abnormal blood flow through the heart. The cause can be harmless or related to structural heart disease.
Common causes include:
-
Innocent murmurs due to increased blood flow during exercise, pregnancy, fever, or anemia
-
Heart valve abnormalities such as stenosis or regurgitation
-
Congenital heart defects present at birth
-
Heart muscle disease
-
Infections of the heart valves, such as endocarditis
-
Rheumatic heart disease
-
Age-related valve degeneration
The exact cause determines whether treatment is needed.
Risk factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of having a heart murmur or an underlying heart condition:
-
Congenital heart defects
-
Family history of heart disease
-
Older age
-
Previous heart infections
-
Rheumatic fever
-
High blood pressure
-
Certain chronic illnesses
-
Pregnancy, due to increased blood volume
Infants and children are also commonly found to have innocent heart murmurs.
Complications
Innocent heart murmurs usually do not cause complications. However, abnormal murmurs linked to heart disease can lead to serious problems if left untreated.
Possible complications include:
-
Heart failure
-
Irregular heart rhythms
-
Increased risk of blood clots
-
Stroke
-
Worsening valve damage
-
Reduced quality of life
Early diagnosis and appropriate management help reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention
Innocent heart murmurs cannot be prevented and do not require treatment. Preventing abnormal heart murmurs focuses on reducing the risk of heart disease and infections.
Preventive measures include:
-
Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels
-
Treating throat infections promptly to prevent rheumatic fever
-
Maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle
-
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol use
-
Managing chronic conditions such as diabetes
-
Attending regular health checkups for early detection
Timely medical evaluation and healthy lifestyle choices play an important role in preventing complications related to heart murmurs.
Advertisement