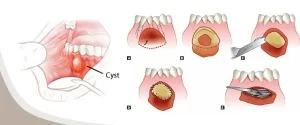
Overview
Jaw tumors and cysts are abnormal growths that develop in the bones or soft tissues of the jaw, most commonly the lower jaw but sometimes the upper jaw. These growths can be benign or, less commonly, malignant. Jaw cysts are typically fluid-filled sacs, while tumors are solid masses. Many jaw tumors and cysts grow slowly and may go unnoticed for a long time, often being discovered during routine dental X-rays or examinations.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the size, location, and type of the tumor or cyst. Some people may have no symptoms in the early stages. When symptoms occur, they may include:
-
Swelling or a lump in the jaw or face
-
Pain or tenderness in the jaw area
-
Loosening or displacement of teeth
-
Difficulty chewing or opening the mouth
-
Numbness or tingling of the lips, chin, or gums
-
Changes in bite or facial appearance
Infections or rapid growth may worsen symptoms.
Causes
Jaw tumors and cysts can arise from different tissues involved in tooth development or jaw formation. Common causes include:
-
Developmental abnormalities related to tooth-forming tissues
-
Impacted or unerupted teeth
-
Chronic dental infections or inflammation
-
Genetic conditions affecting jaw or bone development
-
Abnormal cell growth in jawbone or surrounding tissues
In many cases, the exact cause is not clearly identified.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the likelihood of developing jaw tumors or cysts:
-
Impacted wisdom teeth or other unerupted teeth
-
Poor oral hygiene or untreated dental infections
-
Previous jaw trauma or surgery
-
Certain genetic syndromes
-
Long-term tobacco use
Regular dental checkups help identify risk factors early.
Complications
If left untreated, jaw tumors and cysts can lead to complications:
-
Destruction or weakening of the jawbone
-
Tooth loss or damage to surrounding teeth
-
Facial deformity or asymmetry
-
Nerve damage causing numbness or altered sensation
-
Recurrent infections
-
Rare progression to malignant tumors, depending on the type
Early diagnosis reduces the risk of serious complications.
Prevention
Not all jaw tumors and cysts can be prevented, but certain measures may lower risk and support early detection:
-
Maintaining good oral hygiene
-
Regular dental and oral health checkups with X-rays when recommended
-
Prompt treatment of dental infections and impacted teeth
-
Avoiding tobacco use
-
Following up on jaw pain, swelling, or unexplained oral changes
Early evaluation and appropriate treatment are key to preventing complications and preserving jaw function.
Advertisement