Overview
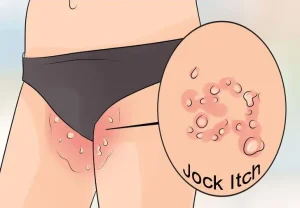
Jock itch, medically known as tinea cruris, is a common fungal skin infection that affects the groin, inner thighs, and surrounding areas. It is caused by dermatophyte fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments. Jock itch is not serious but can be uncomfortable and may recur if not properly treated or prevented.
Symptoms
Symptoms of jock itch usually develop gradually and may include:
-
Itching or burning sensation in the groin area
-
Red, scaly, or cracked skin
-
A rash with a raised, well-defined border
-
Skin that may appear lighter or darker in the affected area
-
Peeling or flaking of the skin
-
Rash that spreads outward while the center may clear
Symptoms often worsen with sweating or physical activity.
Causes
Jock itch is caused by fungal organisms that commonly live on the skin and multiply under favorable conditions. The infection spreads through direct skin contact or by sharing contaminated items such as towels or clothing. Moisture, friction, and poor ventilation in the groin area promote fungal growth.
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of developing jock itch include:
-
Excessive sweating
-
Wearing tight or non-breathable clothing
-
Warm or humid climates
-
Obesity, which increases skin folds
-
Weakened immune system
-
Sharing personal items such as towels
These factors create an environment that supports fungal overgrowth.
Complications
If left untreated or repeatedly irritated, jock itch may lead to complications:
-
Secondary bacterial skin infections
-
Chronic or recurrent fungal infection
-
Spread of infection to other body areas, such as the thighs or buttocks
-
Skin discoloration after healing
Proper treatment reduces the risk of recurrence and complications.
Prevention
Jock itch can often be prevented by maintaining good hygiene and reducing moisture:
-
Keeping the groin area clean and dry
-
Changing out of sweaty clothing promptly
-
Wearing loose-fitting, breathable underwear
-
Avoiding sharing towels or clothing
-
Drying the groin area thoroughly after bathing
-
Treating other fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot, promptly
Consistent preventive measures help reduce the likelihood of jock itch and support healthy skin.
Advertisement