Overview
A kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis, is a serious type of urinary tract infection that affects one or both kidneys. It usually begins in the bladder or urethra and travels upward to the kidneys. Kidney infections require prompt medical treatment, as delayed care can lead to permanent kidney damage or life-threatening complications.
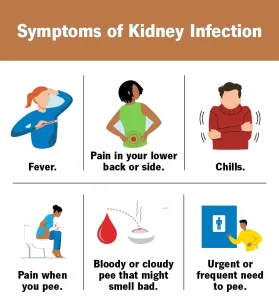
Symptoms
Symptoms of a kidney infection often develop quickly and may be more severe than those of a lower urinary tract infection.
Common symptoms include:
-
Fever and chills
-
Pain in the lower back, side, or groin
-
Pain or burning during urination
-
Frequent or urgent need to urinate
-
Cloudy, dark, or foul-smelling urine
-
Blood in the urine
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Fatigue or general weakness
Causes
Kidney infections are most commonly caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract and spreading to the kidneys.
Primary causes include:
-
Bacterial urinary tract infections, especially from Escherichia coli
-
Blockage of the urinary tract, such as kidney stones
-
Vesicoureteral reflux, where urine flows backward toward the kidneys
-
Use of urinary catheters
-
Spread of infection through the bloodstream in rare cases
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are at higher risk of developing kidney infections.
Risk factors include:
-
Female anatomy, which allows easier bacterial entry
-
Previous urinary tract infections
-
Pregnancy
-
Diabetes
-
Weakened immune system
-
Enlarged prostate in men
-
Structural abnormalities of the urinary tract
-
Long-term catheter use
Complications
Without proper treatment, kidney infections can lead to serious health problems.
Possible complications include:
-
Chronic kidney disease or permanent kidney damage
-
Bloodstream infection leading to sepsis
-
Recurrent kidney infections
-
High blood pressure
-
Pregnancy complications, such as preterm birth
Prevention
Many kidney infections can be prevented by reducing the risk of urinary tract infections and addressing underlying causes.
Preventive measures include:
-
Drinking adequate fluids daily
-
Urinating when the urge arises and not delaying
-
Maintaining proper genital hygiene
-
Urinating after sexual activity
-
Managing blood sugar levels in diabetes
-
Treating urinary tract infections promptly and completely
If you want, I can also create diagnosis, treatment, or recovery sections in the same SEO-optimized WordPress-ready format.
Advertisement