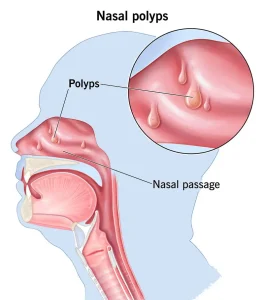
Overview
Nasal polyps are soft, painless, noncancerous growths that develop on the lining of the nasal passages or sinuses. They result from long-term inflammation and are often associated with conditions such as chronic sinusitis, asthma, or allergies. Nasal polyps vary in size and may occur in clusters, potentially blocking airflow and normal sinus drainage when they become large.
Symptoms
Small nasal polyps may not cause noticeable symptoms. Larger polyps or multiple growths can lead to:
-
Persistent nasal congestion or blockage
-
Runny nose or postnasal drip
-
Reduced or lost sense of smell and taste
-
Facial pressure or headache
-
Snoring or mouth breathing
-
Frequent sinus infections
Symptoms often develop gradually and may worsen over time.
Causes
Nasal polyps are caused by chronic inflammation of the nasal and sinus lining. Ongoing immune responses lead to swelling and fluid accumulation, eventually forming polyps. Conditions that commonly contribute to chronic inflammation include allergies, asthma, recurrent infections, and sensitivity to certain medications. The exact mechanism behind polyp formation is not fully understood.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing nasal polyps:
-
Chronic sinus infections or inflammation
-
Asthma
-
Allergic rhinitis
-
Aspirin sensitivity
-
Certain immune system disorders
-
Family history of nasal polyps
The presence of multiple inflammatory conditions increases risk.
Complications
If untreated, nasal polyps can cause complications:
-
Chronic sinusitis with frequent infections
-
Breathing difficulties due to nasal obstruction
-
Sleep disturbances or sleep apnea
-
Permanent loss or reduction of sense of smell
-
Recurrence after treatment
Proper management helps reduce symptom severity and recurrence.
Prevention
Nasal polyps cannot always be prevented, but certain steps may reduce risk and recurrence:
-
Managing allergies and asthma effectively
-
Using prescribed nasal treatments as directed
-
Avoiding airborne irritants such as smoke and pollutants
-
Practicing good nasal hygiene, including saline rinses
-
Seeking medical care for persistent nasal or sinus symptoms
Consistent treatment of underlying conditions plays a key role in preventing nasal polyps and related complications.
Advertisement