Overview
Oral lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the mucous membranes inside the mouth. It is considered an immune-mediated disorder and may present with periods of flare-ups and remission. Oral lichen planus is not contagious, but it can cause persistent discomfort and requires long-term monitoring due to potential complications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of oral lichen planus vary depending on the form and severity of the condition:
-
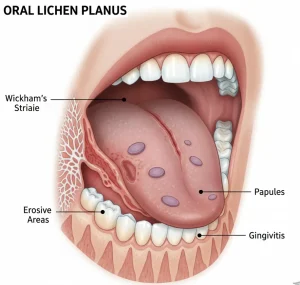
White, lacy or web-like patches on the inner cheeks, tongue, or gums
-
Red, swollen, or inflamed oral tissues
-
Pain or burning sensation in the mouth
-
Mouth sores or ulcers
-
Sensitivity to spicy, acidic, or hot foods
-
Dry mouth or altered taste sensation
-
Bleeding gums in more severe cases
Causes
The exact cause of oral lichen planus is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response:
-
Autoimmune reaction targeting oral mucosal cells
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Stress or emotional factors that may trigger flare-ups
-
Certain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or blood pressure medicines
-
Dental materials or oral allergens
-
Viral infections in some cases
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing oral lichen planus:
-
Middle-aged and older adults
-
Female gender
-
Personal or family history of autoimmune diseases
-
Chronic stress
-
Exposure to triggering medications or dental materials
-
Poor oral hygiene or existing oral irritation
Complications
Oral lichen planus can lead to complications, especially if symptoms are severe or persistent:
-
Chronic pain and discomfort
-
Difficulty eating or speaking
-
Secondary oral infections
-
Gum disease or tooth loss due to inflammation
-
Increased risk of oral cancer with long-standing disease
Prevention
There is no definitive way to prevent oral lichen planus, but symptom control and risk reduction are possible:
-
Maintaining good oral hygiene
-
Avoiding known triggers such as spicy or irritating foods
-
Managing stress effectively
-
Regular dental and medical check-ups
-
Monitoring lesions for changes and seeking prompt evaluation if symptoms worsen
Advertisement