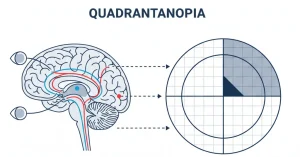
Overview
Quadrantanopia is a visual field defect in which one-quarter of the visual field is lost in one or both eyes. It usually results from damage to specific parts of the brain involved in visual processing rather than a problem with the eyes themselves. The condition can affect daily activities such as reading, driving, and navigating surroundings, depending on which quadrant of vision is missing.
Symptoms
The symptoms of quadrantanopia vary based on the affected visual quadrant and whether one or both eyes are involved. Common symptoms include:
-
Loss of vision in the upper or lower quarter of the visual field
-
Difficulty reading or seeing objects on one side
-
Bumping into objects on the affected side
-
Problems with depth perception or spatial awareness
-
Eye strain or headaches due to visual compensation
Causes
Quadrantanopia is caused by damage to the visual pathways in the brain, particularly the optic radiation or occipital lobe. Common causes include:
-
Stroke affecting the visual processing areas
-
Traumatic brain injury
-
Brain tumors or space-occupying lesions
-
Infections or inflammation of the brain
-
Neurodegenerative disorders affecting visual pathways
-
Complications following brain surgery
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing quadrantanopia, including:
-
History of stroke or transient ischemic attack
-
Head trauma or accidents involving brain injury
-
High blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease
-
Brain tumors or neurological disorders
-
Advanced age
-
Smoking and poor vascular health
Complications
If left unmanaged, quadrantanopia can lead to various complications that affect quality of life:
-
Increased risk of falls and accidents
-
Difficulty driving or loss of driving eligibility
-
Reduced independence in daily activities
-
Emotional distress, anxiety, or depression
-
Challenges with work or academic performance
Prevention
Prevention focuses on reducing the risk of underlying conditions that can cause brain damage:
-
Managing blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol levels
-
Seeking prompt medical care for stroke symptoms
-
Using protective gear to prevent head injuries
-
Avoiding smoking and maintaining a healthy lifestyle
-
Regular medical check-ups for early detection of neurological conditions
Advertisement