Overview
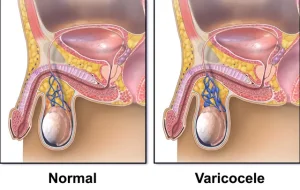
Varicocele is a condition characterized by enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins that occur in the legs. These veins are part of the pampiniform plexus, which helps regulate blood flow and temperature around the testicles. Varicoceles usually develop during puberty and are more commonly found on the left side of the scrotum.
The condition is often harmless and may not cause symptoms. However, in some cases, varicocele can affect testicular function, leading to discomfort, testicular shrinkage, or fertility problems.
Symptoms
Many individuals with varicocele have no noticeable symptoms. When symptoms are present, they may include:
-
Dull or aching pain in the scrotum
-
Feeling of heaviness or dragging sensation in the testicles
-
Visible or palpable enlarged veins in the scrotum, often described as a “bag of worms”
-
Discomfort that worsens with standing or physical activity
-
Improvement of symptoms when lying down
-
Reduced testicular size on the affected side in some cases
-
Fertility issues discovered during evaluation
Causes
Varicocele occurs when the valves inside the scrotal veins do not function properly. These faulty valves allow blood to pool, causing the veins to enlarge.
Contributing factors include:
-
Abnormal blood flow within the testicular veins
-
Increased pressure in the veins of the scrotum
-
Anatomical differences in the left testicular vein drainage
-
Impaired venous valve function
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing varicocele:
-
Puberty and adolescence
-
Taller body height
-
Family history of varicocele
-
Conditions that increase abdominal pressure
-
Previous scrotal or abdominal issues affecting blood flow
Complications
Although often benign, varicocele can lead to complications in some individuals:
-
Decreased sperm quality and quantity
-
Male infertility
-
Testicular atrophy or shrinkage
-
Chronic scrotal pain or discomfort
-
Hormonal imbalances affecting testicular function
Prevention
There is no proven way to prevent varicocele, as it is related to vein anatomy and blood flow patterns. However, early detection and monitoring can help prevent complications.
Preventive and supportive measures include:
-
Regular self-examination of the testicles
-
Medical evaluation for persistent scrotal pain or swelling
-
Early fertility assessment when concerns arise
-
Following medical advice for monitoring or treatment when needed
Timely diagnosis and appropriate management can help preserve testicular health and fertility.
Advertisement