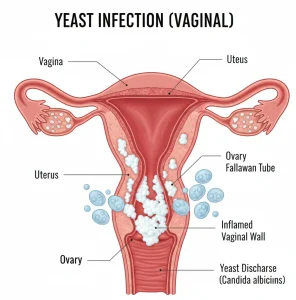
Overview
A yeast infection is a common fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of yeast, most often Candida albicans. Yeast normally lives on the skin and inside the body in small amounts without causing harm. When the balance of microorganisms is disrupted, yeast can multiply and lead to infection.
Yeast infections most commonly affect the vagina, mouth, skin folds, and diaper area in infants. Vaginal yeast infections are especially common in women and can occur at any age. Although uncomfortable, most yeast infections are not serious and can be treated effectively with antifungal medicines.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a yeast infection vary depending on the area of the body involved. Common symptoms include:
-
Itching, burning, or irritation in the affected area
-
Redness and swelling of the skin or mucous membranes
-
Thick, white discharge that may resemble cottage cheese, especially in vaginal yeast infections
-
Pain or discomfort during urination or sexual activity in vaginal infections
-
White patches inside the mouth or on the tongue in oral yeast infections
-
Rash with defined edges and possible small satellite spots on nearby skin
Causes
Yeast infections occur when the natural balance between yeast and bacteria is disrupted, allowing yeast to grow excessively. Factors that can contribute to this imbalance include:
-
Use of antibiotics, which reduce healthy bacteria
-
Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or from birth control pills
-
High blood sugar levels, including those related to diabetes
-
A weakened immune system due to illness or medications
-
Prolonged moisture or warmth on the skin
Risk factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing a yeast infection, including:
-
Pregnancy
-
Diabetes, especially if poorly controlled
-
Recent antibiotic use
-
Wearing tight or non-breathable clothing
-
Use of corticosteroids or immune-suppressing medications
-
Infancy, particularly in diapered babies
Complications
Most yeast infections clear with proper treatment. However, complications may occur, such as:
-
Recurrent yeast infections, defined as four or more in one year
-
Severe symptoms in people with weakened immune systems
-
Spread of infection to other areas of the body
-
Increased discomfort and skin breakdown if left untreated
Prevention
Steps to help reduce the risk of yeast infections include:
-
Keeping the affected areas clean and dry
-
Wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing and cotton underwear
-
Avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use
-
Managing blood sugar levels if you have diabetes
-
Avoiding scented hygiene products that may irritate sensitive tissues
Prompt treatment and preventive measures can help manage symptoms and reduce the chance of recurrence.
Advertisement