Overview
Aspergillosis is an infection caused by a mold known as aspergillus, which is a type of fungus commonly found in the environment. The illnesses caused by aspergillosis usually affect the respiratory system, though symptoms and severity can vary widely. Some forms are mild, while others can be life-threatening.
Aspergillus mold is found both indoors and outdoors. Most strains are harmless to people with healthy immune systems. However, certain strains can cause serious illness when fungal spores are inhaled by people with weakened immune systems, underlying lung disease or asthma.
In some individuals, exposure to aspergillus triggers an allergic reaction. Others may develop lung infections that range from mild to severe. The most serious form is invasive aspergillosis, which occurs when the infection spreads beyond the lungs into blood vessels and other organs.
Treatment depends on the type of aspergillosis and may include careful monitoring, antifungal medications or, in rare cases, surgery.
Symptoms
Symptoms of aspergillosis vary depending on the type of condition that develops.
Some people experience an allergic response, while others develop localized or invasive infections.
Allergic reaction
People with asthma or cystic fibrosis may develop an allergic reaction to aspergillus mold, known as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Symptoms may include:
-
Fever
-
Wheezing
-
Cough that may produce mucus or blood
-
Worsening asthma symptoms
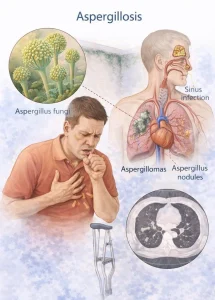
Aspergilloma
Certain chronic lung diseases can create air spaces in the lungs called cavities. These may occur with conditions such as emphysema, tuberculosis or advanced sarcoidosis. When aspergillus infects these cavities, the fungus can form tangled clumps known as aspergillomas, or fungus balls.
At first, aspergillomas may cause no symptoms or only a mild cough. Over time, they can worsen lung disease and lead to:
-
A persistent cough that often brings up blood
-
Fatigue
-
Shortness of breath
-
Unintentional weight loss
-
Wheezing
Invasive aspergillosis
Invasive aspergillosis is the most severe form of the disease. It occurs when the infection spreads quickly from the lungs to other organs, such as the brain, heart, kidneys or skin. This form occurs almost exclusively in people with severely weakened immune systems, including those undergoing chemotherapy or bone marrow transplantation.
Symptoms vary depending on the organs involved but commonly include:
-
A cough that brings up blood
-
Chest or joint pain
-
Fever and chills
-
Headaches or eye-related symptoms
-
Shortness of breath
-
Skin lesions
Other types of aspergillosis
Aspergillus can also affect areas outside the lungs, such as the sinuses. Sinus involvement may cause nasal congestion, drainage that may contain blood, facial pain, headache and fever.
When to see a doctor
If you have asthma or cystic fibrosis, contact your healthcare professional if you notice changes in your breathing. Even if aspergillosis is not the cause, breathing problems should be evaluated.
Seek immediate medical care if you have a weakened immune system and develop an unexplained fever, shortness of breath or a cough that brings up blood. In suspected cases of invasive aspergillosis, treatment often begins before test results confirm the diagnosis.
Causes
Aspergillus mold is widespread and difficult to avoid. Outdoors, it is commonly found in soil, decaying leaves, compost and grain crops. Indoors, it may be present in damp or dusty environments.
For people with healthy immune systems, inhaling aspergillus spores rarely causes problems because immune cells quickly destroy them. In people with weakened immune defenses, however, the body may not be able to eliminate the spores. This allows the fungus to grow in the lungs and, in severe cases, spread to other parts of the body.
Aspergillosis does not spread from person to person.
Risk factors
The risk of developing aspergillosis depends largely on immune system health and lung condition.
Factors that increase risk include:
-
A weakened immune system due to organ transplantation, chemotherapy, blood cancers or advanced AIDS
-
Low white blood cell levels caused by chemotherapy, leukemia or inherited immune disorders such as chronic granulomatous disease
-
Lung cavities caused by conditions like tuberculosis, emphysema or sarcoidosis
-
Asthma or cystic fibrosis, especially when symptoms are severe or difficult to control
-
Long-term use of corticosteroid medications, which can suppress immune function
Complications
Complications of aspergillosis vary by type and severity of infection.
Possible complications include:
-
Severe lung bleeding, which can occur with aspergillomas and invasive aspergillosis and may be life-threatening
-
Spread of infection to other organs, including the brain, heart and kidneys, which occurs in invasive aspergillosis and can be fatal if not treated promptly
Prevention
Complete avoidance of aspergillus exposure is not possible, as the mold is common in the environment. However, people at high risk can take steps to reduce exposure.
If you have a weakened immune system or are undergoing chemotherapy or transplantation, avoid places where mold is likely to be present, such as construction sites, compost piles and grain storage facilities. Your healthcare professional may recommend wearing a protective face mask to reduce inhalation of aspergillus spores and other airborne infectious agents.
Advertisement