Overview
Diagnosis
Diagnosing aspergillosis, including aspergilloma or invasive aspergillosis, can be challenging because Aspergillus is common in the environment. Its symptoms are similar to other lung conditions, such as tuberculosis, and the fungus can be difficult to distinguish from other molds under a microscope.
Healthcare professionals often use a combination of tests to confirm the diagnosis:
Imaging tests
-
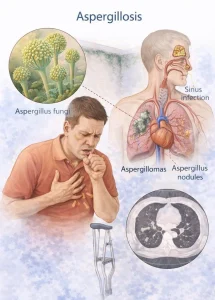
Chest X-ray or CT scan. These can reveal a fungal mass called an aspergilloma and detect signs of invasive aspergillosis or allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis.
Respiratory secretion tests
-
Sputum analysis. A sample of mucus is stained and examined for Aspergillus fibers. The sample can also be cultured to help confirm the presence of the fungus.
Tissue and blood tests
-
Skin testing and blood tests. A small amount of Aspergillus antigen may be injected into the skin. If antibodies are present in the blood, a red bump develops at the injection site. Blood tests can also detect elevated antibody levels, indicating an allergic response.
Biopsy
-
In some cases, a tissue sample from the lungs or sinuses is examined under a microscope to confirm invasive aspergillosis.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type and severity of aspergillosis:
Observation
-
Simple, single aspergillomas often do not require active treatment. These fungal masses are monitored with regular imaging. If the condition worsens, antifungal medications may be considered.
Oral corticosteroids
-
Used for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, especially in people with asthma or cystic fibrosis. Steroids help reduce inflammation and prevent worsening lung function. Antifungal medicines may sometimes be combined with corticosteroids to reduce steroid doses.
Antifungal medicines
-
Standard treatment for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Voriconazole is commonly preferred, while amphotericin B is another option. These medicines can have serious side effects, including kidney or liver damage, and may interact with other medications.
Surgery
-
If an aspergilloma causes lung bleeding, surgical removal is often the best option because antifungal medicines alone are not effective against fungal masses.
Embolization
-
A temporary procedure to stop bleeding caused by an aspergilloma. A material is injected to block the blood supply to the affected area. Bleeding may recur over time, so this is usually a temporary solution.
Advertisement