Overview
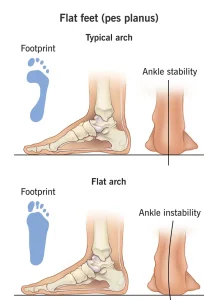
Flatfeet, also known as fallen arches, is a condition in which the arches of the feet are low or absent, causing the soles to touch the ground fully or nearly fully when standing. Flatfeet can be present from childhood or develop later in life due to injury, aging, or medical conditions. Many people with flatfeet do not experience symptoms, while others may have foot pain or problems with walking and posture.
Symptoms
Symptoms of flatfeet vary depending on severity and whether the condition causes strain on the feet or legs:
-
Feet that appear flat when standing
-
Foot pain, especially in the arch or heel
-
Swelling along the inside of the ankle
-
Pain that worsens with prolonged standing or walking
-
Tired or aching feet
-
Difficulty standing on tiptoes in some cases
Some individuals may also experience knee, hip, or lower back discomfort.
Causes
Flatfeet can result from several factors affecting the structure or function of the foot:
-
Inherited foot structure
-
Weak or stretched tendons, especially the posterior tibial tendon
-
Aging-related wear and tear
-
Foot or ankle injuries
-
Arthritis or inflammatory conditions
-
Conditions affecting nerves or muscles
In children, flatfeet often improve as the arches develop with growth.
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing flatfeet include:
-
Family history of flatfeet
-
Obesity
-
Diabetes
-
Pregnancy
-
Aging
-
Repetitive stress on the feet
These factors may contribute to loss of arch support over time.
Complications
While flatfeet are often harmless, complications can occur when the condition causes strain:
-
Chronic foot pain
-
Ankle instability
-
Knee, hip, or lower back pain
-
Difficulty walking or standing for long periods
-
Increased risk of foot injuries
Proper support and care help reduce the risk of long-term problems.
Prevention
Flatfeet cannot always be prevented, but symptoms and complications may be minimized:
-
Wearing supportive footwear
-
Using arch supports or orthotics if recommended
-
Maintaining a healthy body weight
-
Avoiding prolonged standing without support
-
Strengthening foot and ankle muscles through exercise
Early attention to foot discomfort can help manage flatfeet effectively and prevent complications.
Advertisement