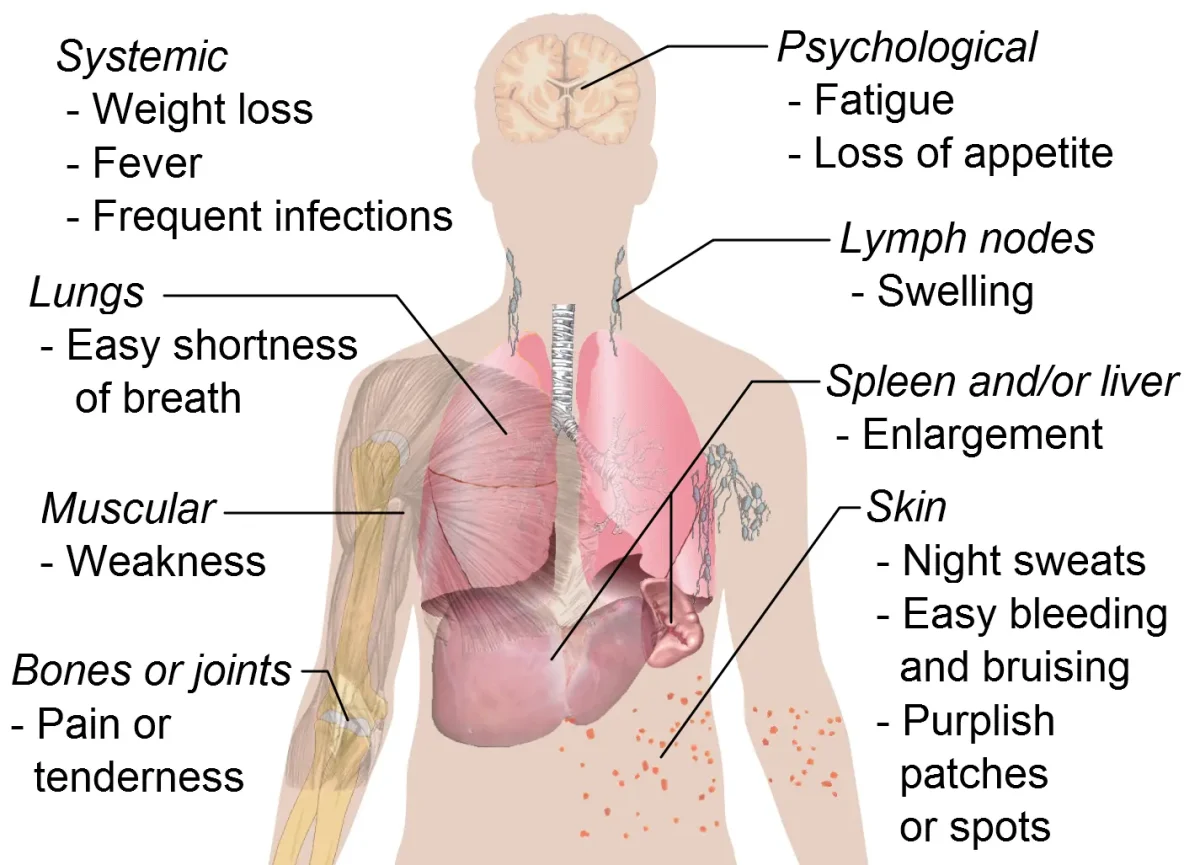
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, where blood cells are produced. It occurs when abnormal white blood cells grow uncontrollably and crowd out healthy blood cells. These cancerous cells interfere with the body’s ability to fight infections, carry oxygen, and control bleeding. Leukemia can develop suddenly or progress slowly over time, depending on …
Kidney Cancer
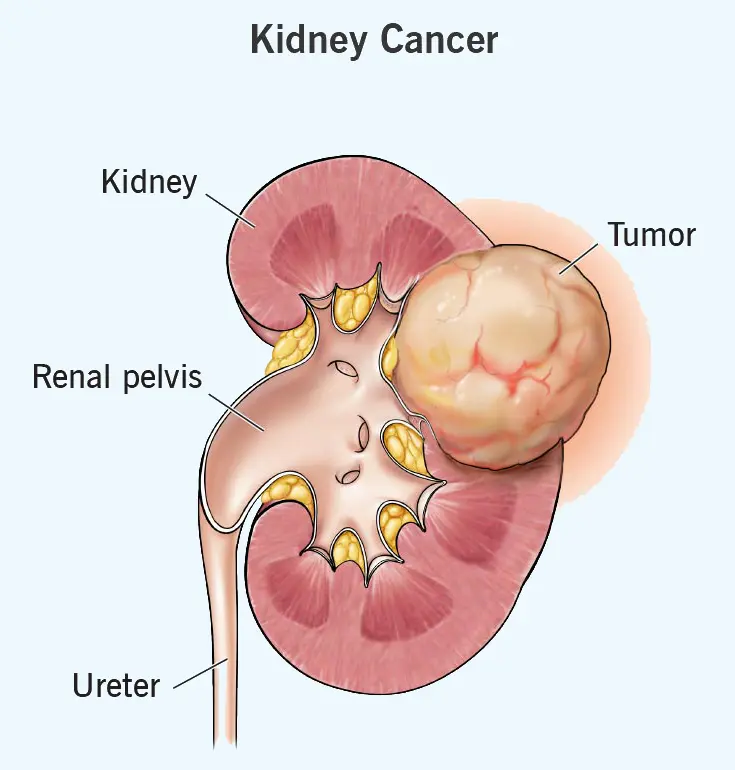
Kidney cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the kidney. The most common type in adults is renal cell carcinoma (RCC). It often develops silently and may be discovered incidentally during imaging for other reasons. Types Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) – ~90% of adult cases Clear cell (most common) Papillary Chromophobe Transitional (Urothelial) …
Hurthle Cell Cancer
Hurthle cell cancer is a rare and aggressive type of thyroid cancer that develops from Hurthle cells, which are specialized cells found in the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck and plays an important role in regulating metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. Hurthle cell cancer is considered a variant of …
Hodgkin Lymphoma (Hodgkin Disease)
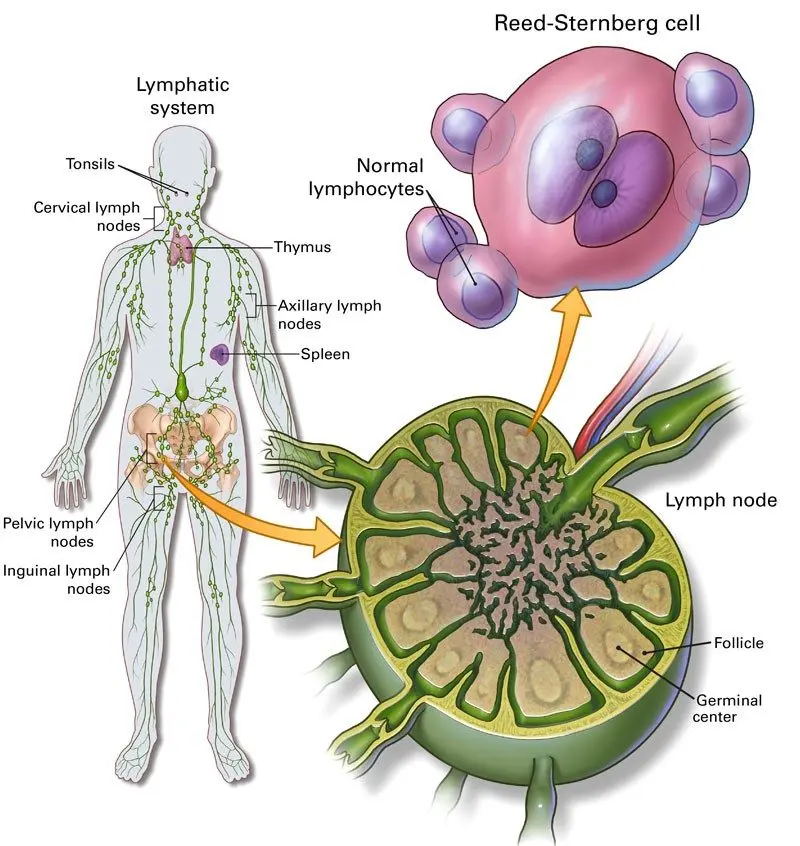
Hodgkin Lymphoma, also known as Hodgkin Disease, is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is part of the immune system and includes lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, and lymph vessels. This cancer develops when certain white blood cells called lymphocytes grow abnormally and form tumors in the lymph nodes. A key feature of …
Hairy Cell Leukemia
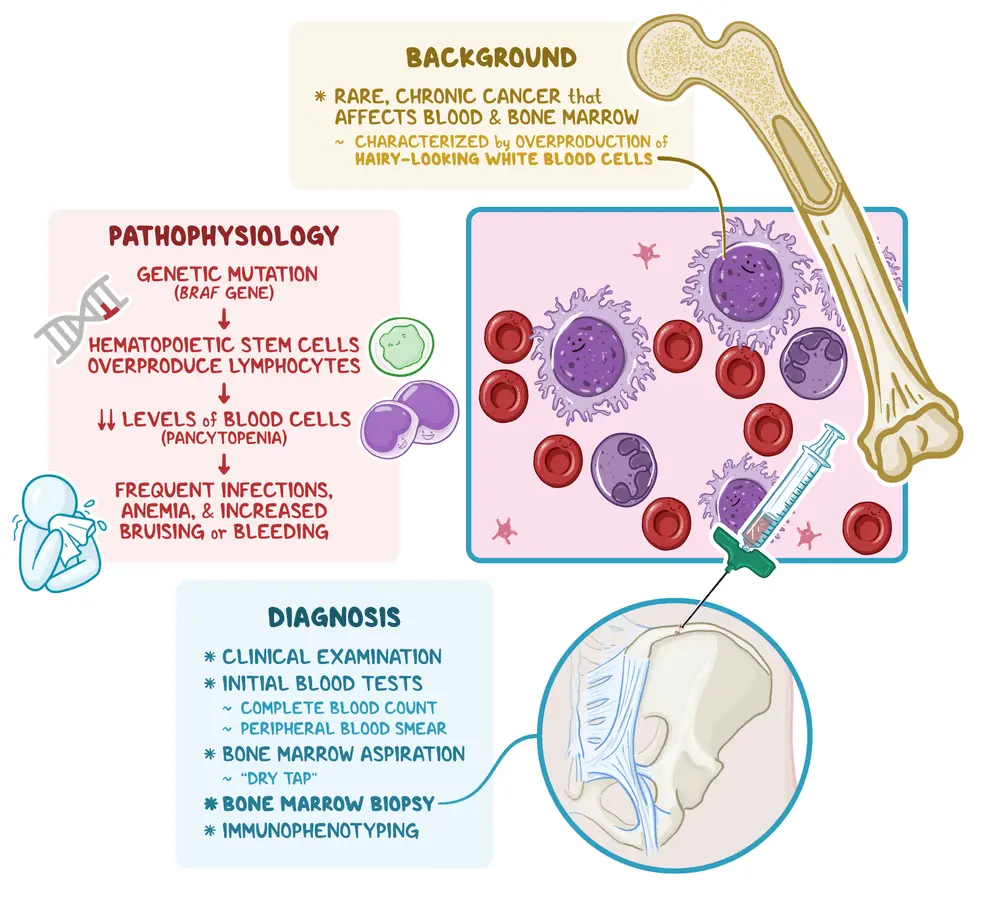
Hairy cell leukemia is a rare, slow-growing cancer of the blood and bone marrow that affects a type of white blood cell called B lymphocytes. The condition gets its name from the fine, hair-like projections seen on the surface of the abnormal cells under a microscope. Hairy cell leukemia typically progresses slowly and is most often diagnosed in middle-aged or …
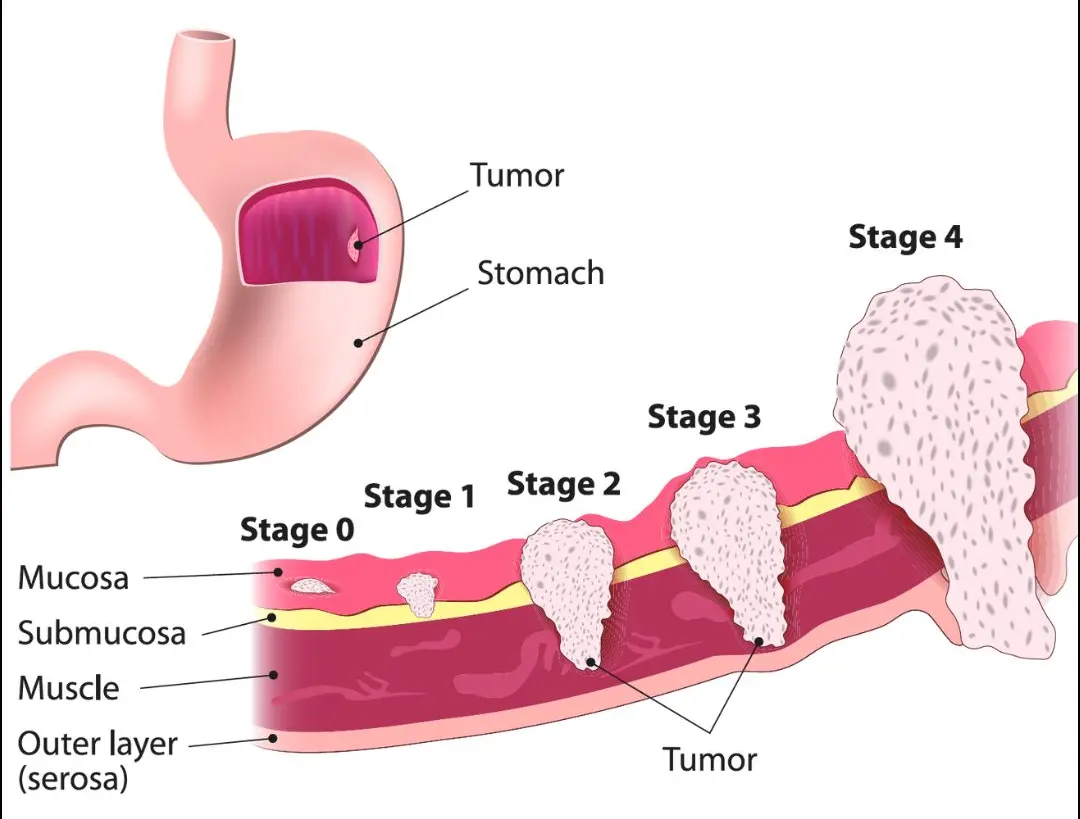
Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, occurs when abnormal cells form in the lining of the stomach and grow uncontrollably. It often develops slowly over several years and may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages. Stomach cancer can spread to nearby organs, lymph nodes, or distant parts of the body if left untreated. Early detection significantly improves …
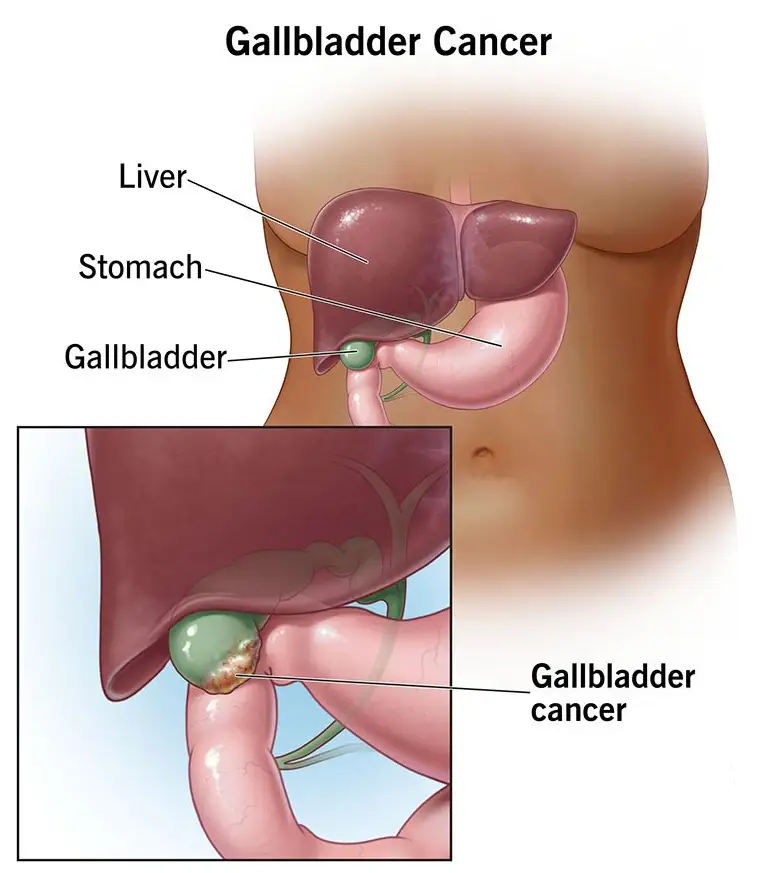
Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer is a rare but serious type of cancer that begins in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile. This cancer often develops silently, with few or no symptoms in its early stages, which is why it is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage. Gallbladder cancer is more common in older adults and tends …
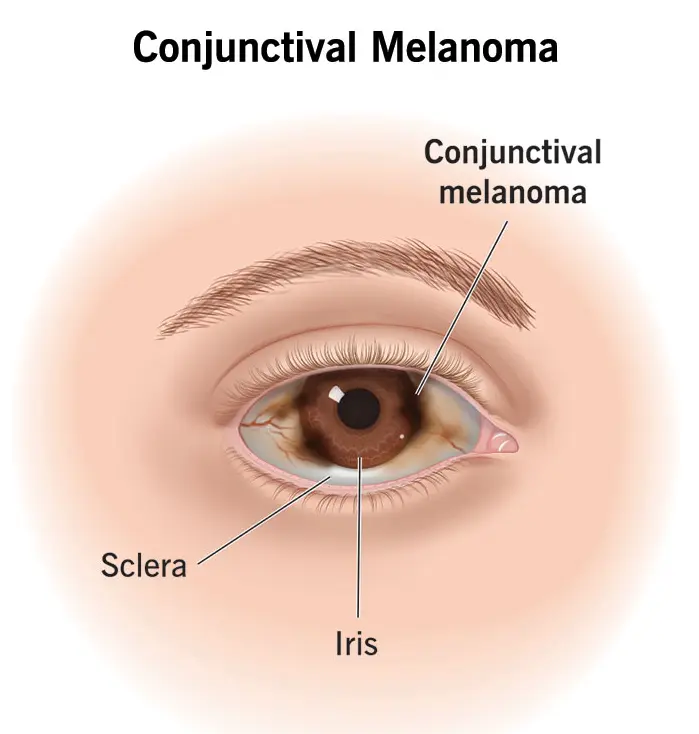
Eye Melanoma
Eye melanoma, also known as ocular melanoma, is a rare but serious type of cancer that develops in the pigment-producing cells of the eye. It most commonly affects the uvea, which includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Eye melanoma can occur without obvious early symptoms and may be detected during routine eye examinations. Early diagnosis is important because the …
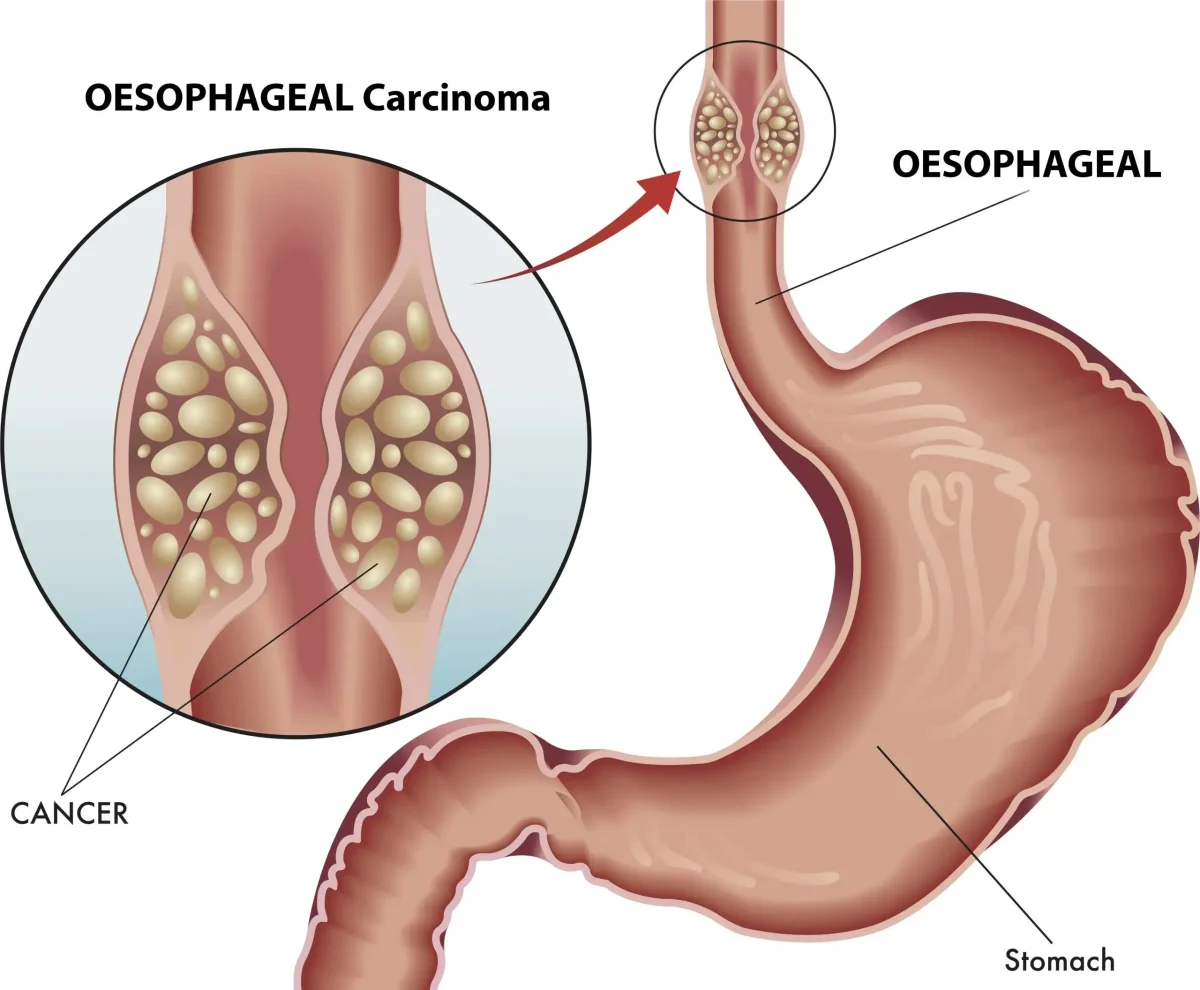
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is a malignant tumor that develops in the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries food and liquids from the throat to the stomach. It commonly begins in the inner lining of the esophagus and can grow outward over time. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, each associated with different risk factors. Esophageal cancer is …
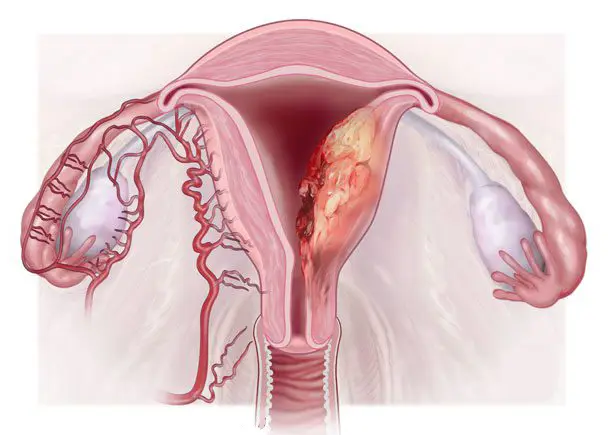
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. It is the most common cancer of the female reproductive system. This cancer is often detected early because it frequently causes noticeable symptoms, especially abnormal vaginal bleeding. Early diagnosis generally leads to effective treatment and favorable outcomes. Symptoms Symptoms of endometrial cancer …