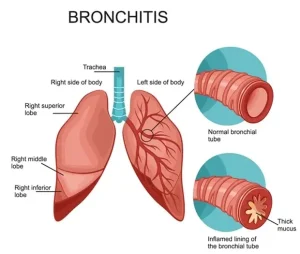
Overview
Bronchitis is a condition in which the bronchial tubes that carry air to and from the lungs become inflamed. This inflammation leads to increased mucus production and narrowed airways, making breathing more difficult. Bronchitis can be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis is usually caused by an infection and improves within a few weeks, while chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition often linked to smoking or prolonged exposure to irritants.
Symptoms
Symptoms of bronchitis can vary depending on whether the condition is acute or chronic. Common symptoms include:
-
Persistent cough, often producing mucus
-
Chest discomfort or tightness
-
Shortness of breath, especially with activity
-
Wheezing
-
Fatigue
-
Mild fever and chills in acute cases
Chronic bronchitis is characterized by a productive cough that lasts for months and may recur over several years.
Causes
Bronchitis occurs when the lining of the bronchial tubes becomes irritated or infected. Common causes include:
-
Viral infections, which are the most common cause of acute bronchitis
-
Bacterial infections in some cases
-
Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
-
Long-term exposure to air pollution, dust, or chemical fumes
-
Repeated respiratory infections
Risk factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing bronchitis:
-
Smoking, the primary risk factor for chronic bronchitis
-
Exposure to air pollutants or workplace irritants
-
Weakened immune system
-
Frequent respiratory infections
-
Older age or very young age
Complications
Most cases of acute bronchitis resolve without complications, but problems can occur in some situations:
-
Pneumonia, especially in older adults or those with weakened immunity
-
Worsening of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
-
Persistent cough lasting several weeks
-
Reduced lung function in chronic cases
Early evaluation is important if symptoms are severe or long-lasting.
Prevention
Certain steps can help reduce the risk of bronchitis:
-
Avoiding smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
-
Using protective equipment when exposed to dust or fumes
-
Practicing good hand hygiene to prevent infections
-
Staying up to date with recommended vaccinations
-
Maintaining overall lung health through regular physical activity
Prompt care and lifestyle changes play an important role in preventing recurrent or chronic bronchitis.
Advertisement