Overview
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It primarily affects the genital tract but can also infect the rectum, throat, and eyes. Gonorrhea often causes mild symptoms or none at all, especially in women, which increases the risk of unknowingly spreading the infection. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are important to prevent complications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gonorrhea may appear within a few days to weeks after exposure, though many people remain asymptomatic. When symptoms occur, they may include:
-
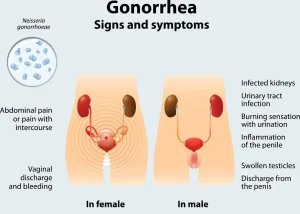
Pain or burning sensation during urination
-
Thick white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis or vagina
-
Increased vaginal discharge
-
Vaginal bleeding between periods
-
Pain or swelling in one or both testicles
-
Rectal pain, discharge, or bleeding
-
Sore throat in cases of throat infection
Symptoms can vary based on the site of infection.
Causes
Gonorrhea is caused by infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria. The infection spreads through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex, with an infected person. The bacteria can infect mucous membranes of the reproductive tract, rectum, throat, or eyes.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of contracting gonorrhea, including:
-
Unprotected sexual activity
-
Multiple sexual partners
-
Having a new sexual partner
-
History of other sexually transmitted infections
-
Inconsistent condom use
Young adults and adolescents are at higher risk due to higher rates of exposure.
Complications
If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to serious health complications. Possible complications include:
-
Pelvic inflammatory disease in women, which can cause infertility
-
Epididymitis in men, leading to testicular pain and infertility
-
Increased risk of HIV transmission
-
Joint infections or bloodstream infection in rare cases
-
Pregnancy complications and newborn infection during childbirth
Early treatment greatly reduces the risk of long-term complications.
Prevention
Gonorrhea can be prevented through safe sexual practices and regular screening:
-
Using condoms consistently and correctly
-
Limiting the number of sexual partners
-
Regular testing for sexually transmitted infections
-
Prompt treatment of infected individuals and their partners
-
Avoiding sexual contact until treatment is completed
Preventive measures and early medical care are essential to control the spread of gonorrhea and protect reproductive health.
Advertisement