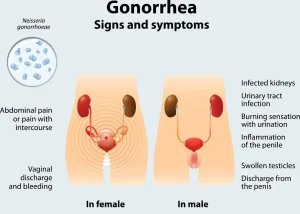
Overview
Diagnosis
Gonorrhea can sometimes be initially detected with at-home tests, but a confirmed diagnosis requires evaluation by a healthcare professional. Diagnosis typically involves analyzing samples from affected areas:
-
Urine test: Detects bacteria in the urethra
-
Swab test: A swab of the throat, urethra, vagina, or rectum can collect bacteria for laboratory analysis
Healthcare professionals may also recommend testing for other sexually transmitted infections, including:
-
Chlamydia: Often occurs alongside gonorrhea
-
HIV: Recommended for anyone diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection
-
Additional STI tests depending on individual risk factors
Treatment
Treatment for adults
-
Gonorrhea is treated with antibiotics. The CDC recommends ceftriaxone, given as an injection, due to rising antibiotic resistance
-
Avoid sexual activity for at least seven days after treatment to prevent spreading the infection
-
Retesting is recommended three months after treatment to ensure reinfection has not occurred
Treatment for sexual partners
-
Sexual partners from the last 60 days should be screened and treated, even if asymptomatic
-
Wait at least seven days after your partner is treated before resuming sexual activity
Treatment for newborns
-
Babies born to someone with gonorrhea who develop the infection can be treated with antibiotics
Effective treatment and partner management are essential to prevent reinfection and further spread of gonorrhea.
Advertisement