Overview
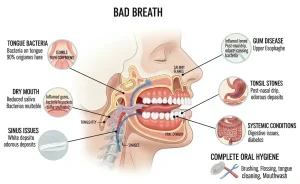
Bad breath, also known as halitosis, is a common condition characterized by an unpleasant odor coming from the mouth. It can be temporary or persistent and may affect people of all ages. In many cases, bad breath is related to oral hygiene issues, but it can also be a sign of underlying medical conditions. Although often not serious, chronic bad breath can cause social discomfort and may require medical or dental evaluation.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of bad breath is an unpleasant or foul-smelling odor when breathing out through the mouth or nose. The odor may vary in intensity and quality. Additional symptoms that may be associated include:
-
Dry mouth or a sticky feeling in the mouth
-
Bad taste that persists despite brushing
-
Coated or white appearance on the tongue
-
Signs of gum disease, such as bleeding or swollen gums
Symptoms may be more noticeable in the morning or after long periods without eating or drinking.
Causes
Bad breath can result from a variety of oral and systemic factors. Common causes include:
-
Poor oral hygiene leading to plaque buildup
-
Bacteria on the tongue that produce odor-causing compounds
-
Gum disease or tooth decay
-
Dry mouth due to dehydration or certain medications
-
Consumption of foods such as garlic, onions, or spices
Less commonly, bad breath may be linked to infections of the sinuses, throat, or lungs, as well as digestive or metabolic conditions.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing bad breath. These include:
-
Infrequent brushing and flossing
-
Smoking or use of tobacco products
-
Wearing dental appliances that are not properly cleaned
-
Chronic dry mouth
-
Poorly controlled diabetes or other systemic illnesses
Dietary habits and lifestyle choices can also influence breath odor.
Complications
Bad breath itself does not usually cause physical complications, but persistent halitosis can affect quality of life. Possible complications include social embarrassment, reduced self-confidence, and anxiety in personal or professional interactions. When bad breath is caused by underlying dental or medical conditions, failure to address it may allow those conditions to worsen over time.
Prevention
Good oral and general health practices can help prevent bad breath. Preventive measures include:
-
Brushing teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily
-
Cleaning the tongue to remove bacteria
-
Drinking plenty of water to prevent dry mouth
-
Avoiding tobacco products
-
Scheduling regular dental checkups and cleanings
Managing underlying health conditions and maintaining consistent oral hygiene are key steps in preventing bad breath.
Advertisement