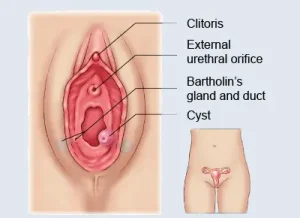
Overview
Bartholin’s cyst is a fluid-filled swelling that develops when one of the Bartholin’s glands, located on either side of the vaginal opening, becomes blocked. These glands produce fluid that helps lubricate the vagina. When the duct is obstructed, fluid builds up and forms a cyst. Bartholin’s cysts are common in women of reproductive age and are often painless, though larger or infected cysts can cause discomfort.
Symptoms
Many Bartholin’s cysts cause no symptoms and are discovered during a routine exam. When symptoms occur, they may include:
-
A painless lump near the vaginal opening
-
Swelling on one side of the vulva
-
Discomfort while walking, sitting, or during sexual activity
-
Redness or tenderness if infection develops
If the cyst becomes infected, it may form an abscess and cause significant pain and fever.
Causes
Bartholin’s cysts develop when the duct of the Bartholin’s gland becomes blocked, preventing normal drainage. Possible causes include:
-
Thickened mucus blocking the gland duct
-
Bacterial infection
-
Local inflammation or trauma
Infections may involve common skin bacteria or organisms associated with sexually transmitted infections.
Risk factors
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing a Bartholin’s cyst. These include:
-
Being of reproductive age
-
Previous Bartholin’s cyst or abscess
-
Sexually transmitted infections
-
Poor genital hygiene
Bartholin’s cysts are uncommon after menopause.
Complications
Most Bartholin’s cysts do not cause complications. However, an infected cyst can form an abscess, leading to severe pain, swelling, and fever. Recurrent cysts or abscesses may require surgical treatment. In rare cases, especially in women over 40, a persistent mass may need evaluation to rule out malignancy.
Prevention
Bartholin’s cysts cannot always be prevented, but certain measures may reduce the risk. Preventive steps include:
-
Practicing good genital hygiene
-
Using condoms to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections
-
Seeking early treatment for vaginal infections or discomfort
Prompt medical evaluation of painful or recurrent cysts can help prevent complications and ensure appropriate care.
Advertisement