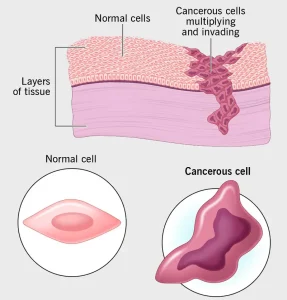
Overview
Cancer is a group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. These cells can form tumors, invade nearby tissues, and spread to distant organs through the blood or lymphatic system, a process known as metastasis. Cancer can develop in almost any organ or tissue and varies widely in behavior, severity, and treatment depending on the type and stage. Early detection and advances in medical care have improved outcomes for many types of cancer.
Symptoms
Cancer symptoms vary based on the type, location, and stage of the disease. Some cancers may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages, while others produce clear warning signs.
Common general symptoms include:
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Persistent fatigue
-
Fever or night sweats
-
Loss of appetite
Symptoms related to specific organs may include:
-
Lumps or swelling
-
Persistent pain
-
Changes in skin appearance or color
-
Changes in bowel or bladder habits
-
Persistent cough or difficulty breathing
-
Unusual bleeding or discharge
Causes
Cancer develops due to genetic changes that disrupt normal cell growth and division. These changes may be inherited or acquired over time due to environmental and lifestyle factors.
Major causes include:
-
Genetic mutations
-
Exposure to carcinogens such as tobacco smoke and chemicals
-
Radiation exposure
-
Certain infections
-
Hormonal influences
In many cases, cancer results from a combination of genetic susceptibility and external factors.
Risk Factors
Risk factors increase the likelihood of developing cancer but do not guarantee that it will occur.
Common risk factors include:
-
Advancing age
-
Family history of cancer
-
Tobacco use
-
Excessive alcohol consumption
-
Obesity and physical inactivity
-
Unhealthy diet
-
Prolonged exposure to sunlight or radiation
-
Certain chronic infections
The presence of one or more risk factors raises risk but does not determine outcome.
Complications
Cancer and its treatments can lead to a range of complications affecting physical and emotional health.
Possible complications include:
-
Spread of cancer to other organs
-
Chronic pain
-
Organ dysfunction
-
Weakened immune system
-
Fatigue and malnutrition
-
Emotional distress, anxiety, or depression
Complications vary depending on cancer type, stage, and treatment approach.
Prevention
While not all cancers can be prevented, many can be reduced through lifestyle changes and preventive care.
Effective prevention strategies include:
-
Avoiding tobacco in all forms
-
Limiting alcohol intake
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
-
Staying physically active
-
Protecting skin from excessive sun exposure
-
Getting recommended vaccinations
-
Participating in age-appropriate cancer screening programs
Early detection through regular screening and awareness of warning signs plays a key role in improving survival and quality of life.
Advertisement