Overview
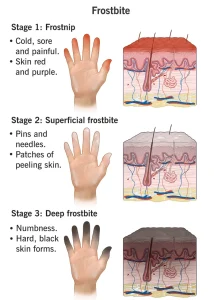
Frostbite is an injury that occurs when skin and underlying tissues freeze due to prolonged exposure to extremely cold temperatures. It most commonly affects exposed body parts such as the fingers, toes, ears, nose, and cheeks. Frostbite can range from mild superficial injury to severe tissue damage and may lead to permanent damage if not treated promptly.
Symptoms
Symptoms of frostbite depend on the depth and severity of the injury:
-
Cold, numb, or tingling skin
-
Pale, white, or bluish-gray skin color
-
Hard or waxy-looking skin
-
Loss of sensation in the affected area
-
Swelling or blistering after rewarming
-
Severe pain during the rewarming process
In advanced cases, the affected area may become blackened due to tissue death.
Causes
Frostbite develops when exposure to cold temperatures causes blood vessels to constrict, reducing blood flow to the skin and tissues. Common causes include:
-
Prolonged exposure to freezing temperatures
-
Contact with cold metal or liquids
-
Inadequate clothing or protection in cold environments
-
Wind chill increasing heat loss
-
Reduced circulation or immobility
The risk increases the longer the exposure continues.
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of frostbite include:
-
Extreme cold or windy conditions
-
Wearing wet or inadequate clothing
-
Alcohol or drug use that impairs judgment
-
Dehydration
-
Poor circulation
-
Certain medical conditions such as diabetes
These factors can reduce the body’s ability to maintain warmth.
Complications
Frostbite can cause serious and long-term complications:
-
Permanent nerve damage
-
Tissue death and gangrene
-
Increased sensitivity to cold
-
Joint stiffness or chronic pain
-
Infection
-
Possible amputation in severe cases
Early treatment reduces the risk of permanent injury.
Prevention
Frostbite can often be prevented with proper precautions:
-
Wearing layered, insulated, and waterproof clothing
-
Protecting exposed skin with gloves, hats, and face coverings
-
Avoiding prolonged exposure to extreme cold
-
Keeping clothing dry
-
Staying well-nourished and hydrated
-
Limiting alcohol consumption in cold environments
Recognizing early signs of cold injury and seeking shelter promptly help prevent frostbite.
Advertisement