Overview
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. It affects the nose, throat, and sometimes the lungs. The flu can range from mild to severe and may lead to serious complications, especially in young children, older adults, pregnant individuals, and those with weakened immune systems or chronic medical conditions. Influenza typically occurs seasonally and spreads easily from person to person.
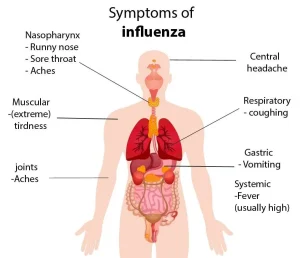
Symptoms
-
Sudden onset of fever and chills
-
Cough, usually dry
-
Sore throat
-
Runny or stuffy nose
-
Muscle or body aches
-
Headache
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
In some cases, vomiting or diarrhea, especially in children
Causes
Influenza is caused by influenza viruses, primarily types A and B, which spread through:
-
Respiratory droplets from coughing, sneezing, or talking
-
Close contact with an infected person
-
Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes
Risk factors
-
Young children and adults over 65 years
-
Pregnancy
-
Chronic medical conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or heart disease
-
Weakened immune system
-
Living in crowded environments
-
Lack of annual influenza vaccination
Complications
-
Pneumonia
-
Bronchitis
-
Sinus and ear infections
-
Worsening of chronic medical conditions
-
Dehydration
-
Hospitalization or death in severe cases
Prevention
-
Annual influenza vaccination
-
Regular handwashing with soap and water
-
Covering mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
-
Avoiding close contact with sick individuals
-
Staying home when ill to prevent spread
-
Maintaining a healthy immune system through proper nutrition, sleep, and exercise
Early treatment with antiviral medications may reduce the severity and duration of influenza if started promptly. Vaccination remains the most effective way to prevent influenza and its complications.
Advertisement