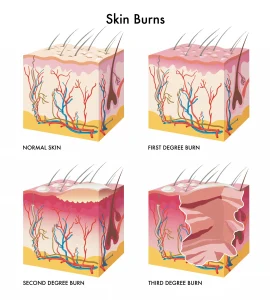
Overview
Burns are injuries to the skin and underlying tissues caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, radiation, or friction. The severity of a burn depends on how deep the injury goes and how much of the body is affected. Burns are commonly classified as minor or severe and can range from mild skin redness to deep tissue damage. Prompt and appropriate care is important to reduce pain, prevent infection, and support proper healing.
Symptoms
Symptoms of burns vary based on the type and severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
-
Redness, pain, and swelling of the skin
-
Blistering or peeling skin
-
White, charred, or leathery-looking skin in severe burns
-
Increased sensitivity or numbness in the affected area
-
Oozing or fluid leakage from blisters
Severe burns may also cause shock, weakness, or difficulty breathing if large areas are involved.
Causes
Burns can occur from many different sources. Common causes include:
-
Heat from flames, hot liquids, steam, or hot objects
-
Chemical exposure from acids, alkalis, or cleaning products
-
Electrical injuries from faulty wiring or lightning
-
Radiation from sun exposure or medical treatments
-
Friction from contact with rough surfaces
The cause often influences the type of treatment required.
Risk factors
Certain factors increase the risk of burn injuries:
-
Cooking or working with open flames or hot equipment
-
Unsafe electrical systems or lack of protective gear
-
Occupational exposure to chemicals or heat
-
Young children and older adults, due to reduced reaction time
-
Alcohol or substance use, which can impair judgment
Home and workplace environments play a major role in burn risk.
Complications
Burns can lead to complications, especially if they are severe or improperly treated:
-
Skin infections and delayed wound healing
-
Scarring or changes in skin appearance
-
Loss of mobility if joints are affected
-
Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance in large burns
-
Breathing problems if smoke or hot air is inhaled
Severe burns may require long-term medical care and rehabilitation.
Prevention
Many burn injuries can be prevented through safety measures:
-
Using caution when handling hot liquids and appliances
-
Installing smoke detectors and fire safety equipment
-
Keeping chemicals stored safely and labeled clearly
-
Using protective clothing and gear at work
-
Practicing sun protection to avoid radiation burns
Awareness and prompt first aid can significantly reduce the severity and long-term impact of burns.
Advertisement