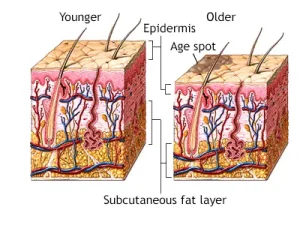
Overview
Age spots — also called liver spots or solar lentigines — are common skin changes caused by long-term sun exposure. While harmless, they may look similar to other skin conditions, so proper diagnosis is important to ensure the right treatment.
Diagnosis of Age Spots
Diagnosing age spots typically involves a visual examination and, if needed, a skin biopsy to rule out other conditions.
-
Visual inspection: Most age spots can be diagnosed simply by examining the skin. Your healthcare provider looks at the size, color, and pattern of the spots. This helps rule out other skin disorders that may need different treatment.
-
Skin biopsy: If there’s any doubt, your doctor may remove a small skin sample for lab testing. A biopsy helps confirm the diagnosis and rule out serious conditions such as Lentigo maligna, a form of skin cancer.
More Information: Skin biopsy
Treatment of Age Spots
If you want to reduce or remove the appearance of age spots, several effective treatment options are available. Since pigment lies in the upper layer of the skin (epidermis), treatments must reach this layer to work effectively.
Medications
Prescription creams can help gradually fade age spots:
-
Bleaching creams (hydroquinone) may be used alone or with retinoids (tretinoin) and a mild steroid.
-
Results may take several months.
-
Temporary side effects can include redness, dryness, itching, or mild burning.
Laser and Intense Pulsed Light Therapy
-
Laser treatments target melanin-producing cells without harming the skin’s surface.
-
Usually requires two to three sessions for best results.
-
Ablative lasers may remove the top layer of skin for more noticeable improvement.
Freezing (Cryotherapy)
-
A cotton-tipped swab with liquid nitrogen is applied for a few seconds to destroy excess pigment.
-
As the skin heals, the treated area lightens.
-
Temporary irritation or scarring may occur.
Dermabrasion and Microdermabrasion
-
Dermabrasion: Sands down the top skin layer using a rotating brush. New skin forms during healing. Redness or swelling may last weeks to months.
-
Microdermabrasion: A gentler option that smooths mild blemishes. Several sessions are needed for visible, but temporary, improvement.
Chemical Peel
-
A chemical solution removes the outer skin layer, allowing new, smoother skin to appear.
-
Side effects can include temporary redness, scarring, or color changes.
-
Multiple treatments may be needed for best results.
Aftercare and Sun Protection
-
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher daily.
-
Wear protective clothing to prevent further sun damage.
-
Most age spot treatments are cosmetic and not covered by insurance.
Important: Because these treatments may have side effects, always consult a qualified dermatologist experienced in the specific procedure you choose.
Advertisement