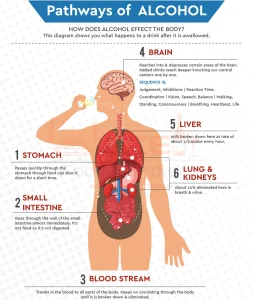
Overview
Diagnosis of Alcohol Poisoning
To confirm alcohol poisoning, a healthcare professional will assess visible symptoms and may recommend specific lab tests to evaluate alcohol toxicity levels.
-
Physical evaluation: Doctors check vital signs such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature.
-
Blood test: Measures blood alcohol concentration (BAC) and can also detect low blood sugar levels, which often occur in alcohol poisoning cases.
-
Urine test: Helps identify alcohol levels and any other toxic substances present in the body.
Important: High BAC levels can be fatal. Immediate medical attention is essential.
Treatment for Alcohol Poisoning
Treatment focuses on supportive care to help the body safely eliminate alcohol and prevent further complications.
-
Continuous monitoring: Medical staff ensure breathing remains stable and prevent choking if vomiting occurs.
-
Oxygen therapy: Helps maintain healthy oxygen levels in the blood.
-
IV fluids: Fluids are given through a vein to prevent dehydration and stabilize electrolytes.
-
Vitamins and glucose: Used to correct low blood sugar and reduce the risk of serious complications such as brain damage.
Additional Treatment: Hemodialysis
-
Hemodialysis: In cases where toxic alcohols like methanol or isopropyl alcohol are ingested, hemodialysis may be required. This mechanically filters toxins from the blood, speeding up the elimination of alcohol and reducing the risk of organ damage.
Prevention Tips
-
Drink responsibly and know your limits.
-
Avoid binge drinking, which is a common cause of alcohol poisoning.
-
Never mix alcohol with medications or drugs that can intensify its effects.
-
Seek emergency help immediately if someone shows symptoms like confusion, vomiting, slow breathing, or unconsciousness.
Advertisement