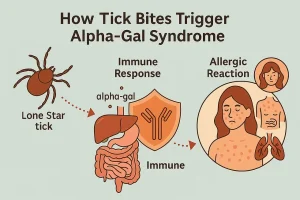
Overview
Diagnosis of Alpha-Gal Syndrome
Diagnosing Alpha-Gal Syndrome begins with a detailed discussion of your symptoms and medical history. Your healthcare professional will perform a physical exam and may recommend a blood test to check for alpha-gal antibodies.
-
A positive blood test shows the presence of alpha-gal antibodies, but having these antibodies does not always mean you have Alpha-Gal Syndrome.
-
Diagnosis is based on a combination of symptoms, medical history, and antibody levels.
Treatment for Alpha-Gal Syndrome
The primary treatment for Alpha-Gal Syndrome is avoiding foods and products that trigger reactions.
1. Avoid Trigger Foods
-
Eliminate red meat and meat-based ingredients from your diet.
-
Carefully read ingredient labels, as meat extracts are sometimes used for flavoring under names that may not be obvious.
-
Your healthcare professional can provide a list of foods and additives to avoid.
2. Be Aware of Animal-Derived Products
Some medical products contain alpha-gal, although reactions are rare:
-
Heart valves from pigs or cows
-
Monoclonal antibodies used to treat certain diseases
-
Heparin (blood-thinning medication)
-
Certain snake bite treatments
3. Managing Allergic Reactions
-
For mild reactions, standard allergy medications may provide relief.
-
For severe reactions, an epinephrine injection and emergency care are required.
-
Many patients carry an epinephrine auto-injector, which delivers a single dose of medicine when pressed against the thigh.
4. Emergency Preparedness
-
After diagnosis, your healthcare professional will likely prescribe an epinephrine auto-injector.
-
They will also teach you how to use it properly for rapid response during a severe reaction.
Key Takeaways
-
Alpha-Gal Syndrome is diagnosed through symptoms, medical history, and blood tests for alpha-gal antibodies.
-
Treatment focuses on avoiding red meat and animal-derived products.
-
Epinephrine auto-injectors are essential for managing severe allergic reactions.
Advertisement