Overview
Bursitis Diagnosis and Treatment Guide
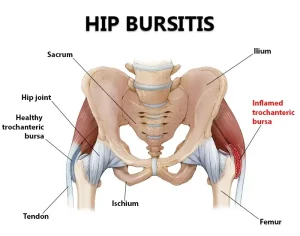
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that cushions your joints. Early diagnosis and proper care can reduce pain and prevent complications.
How Bursitis is Diagnosed
Doctors often diagnose bursitis through a medical history review and physical exam. They may check for joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion limitations.
If needed, additional tests may be ordered:
Imaging Tests
-
X-rays: While X-rays cannot confirm bursitis, they help rule out other causes of joint pain, such as fractures or arthritis.
-
Ultrasound: This can detect inflammation and fluid buildup in the bursa.
-
MRI: Used when bursitis is difficult to diagnose, MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues and helps identify bursitis in complex cases.
Lab Tests
-
Blood tests: Can help identify underlying conditions or infections causing bursitis.
-
Fluid analysis: A sample of fluid from the inflamed bursa may be taken to determine if infection or other factors are present.
Treatment for Bursitis
Most cases of bursitis improve with conservative treatment. Steps to relieve discomfort include:
Conservative Care
-
Rest: Avoid activities that worsen pain.
-
Ice therapy: Apply ice packs to reduce swelling and inflammation.
-
Pain relievers: Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen) can ease pain.
Medications
-
Antibiotics: Prescribed if bursitis is caused by an infection.
-
Corticosteroid injections: A steroid injected into the bursa can rapidly reduce pain and inflammation. Often, a single injection provides lasting relief.
Physical Therapy
-
Exercises and therapy can strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, improving mobility and preventing recurrence.
Assistive Devices
-
Temporary use of a cane or brace can help reduce stress on the inflamed area.
Surgical Options
-
Bursa drainage: In cases of persistent fluid buildup or infection, the bursa may need to be drained surgically.
-
Bursa removal: Rarely, surgery may remove the inflamed bursa entirely if other treatments fail.
Advertisement