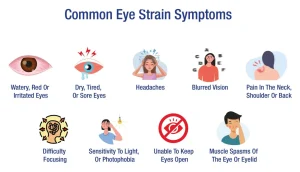
Overview
Diagnosis
Eyestrain diagnosis is typically made through a comprehensive eye examination to rule out other vision problems or underlying conditions.
-
Medical History:
Your eye specialist will ask detailed questions about your symptoms, daily activities, and visual habits, such as screen use or reading time. -
Vision Test:
A standard vision test checks your ability to focus and see clearly at different distances. -
Eye Examination:
A slit-lamp exam or retinal exam may be done to evaluate the overall health of your eyes and identify any issues like dryness, refractive errors, or muscle strain.
Treatment
Eyestrain treatment mainly focuses on adjusting daily habits, improving visual ergonomics, and managing any underlying eye conditions.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments:
-
Modify lighting: Keep the room softly lit when watching TV and ensure adequate task lighting when reading or working.
-
Take regular breaks: Use the 20-20-20 rule — every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
-
Limit screen time: Especially for children, to prevent prolonged visual fatigue.
-
-
Corrective Eyewear:
Wearing glasses or contact lenses designed for specific activities, such as computer use or reading, can reduce eyestrain. Ask your eye specialist about anti-reflective coatings or blue-light filters. -
Artificial Tears:
Use lubricating eye drops to relieve dryness.-
Avoid drops with redness removers.
-
Preservative-free drops can be used frequently; preservative-containing drops should not exceed four uses per day.
-
-
Environmental Changes:
Improve air quality by using a humidifier, adjusting airflow, and avoiding smoke or dry air exposure.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Simple habits can significantly reduce or prevent eyestrain symptoms:
-
Adjust your monitor: Place your screen at arm’s length, with the top slightly below eye level.
-
Reduce glare: Use anti-glare screens, desk lamps, and soft room lighting.
-
Blink often: Frequent blinking helps keep your eyes moist and refreshed.
-
Use document holders: To minimize constant refocusing between paper and screen.
-
Adjust screen settings: Increase text size, reduce brightness, and enhance contrast for comfort.
Alternative Medicine
Some natural remedies may help relieve mild eyestrain:
-
Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil or supplements may improve tear quality and reduce dryness, though more research is needed.
-
Always consult your eye specialist before taking any supplements.
Preparing for Your Appointment
If your eyestrain does not improve with self-care, it’s best to see an eye specialist.
Before your visit:
-
Note your symptoms and their duration.
-
List medications and supplements you take.
-
Track how much time you spend on digital devices and close-up tasks.
-
Prepare questions to ask your doctor.
Possible questions include:
-
What is likely causing my symptoms?
-
Do I need any tests to confirm the diagnosis?
-
What lifestyle changes could help reduce my symptoms?
-
What treatment options or follow-up appointments are recommended?
What to Expect from Your Doctor
Your eye specialist may ask:
-
When did your symptoms start, and how have they changed?
-
How severe is your discomfort?
-
How much time do you spend on screens daily?
-
Do you work in a dry or air-conditioned environment?
-
Does anything trigger or relieve your symptoms?
-
When was your last vision exam?
Advertisement