Overview
Diagnosis
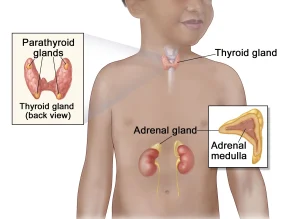
To diagnose multiple endocrine neoplasia, type 2 (MEN 2), your healthcare provider begins with a physical exam and a review of your personal and family medical history. Genetic testing is performed to identify gene changes that cause MEN 2. Additional tests may include:
• Blood tests to measure calcitonin, calcium, and parathyroid hormone levels
• Urine or plasma tests for catecholamines and metanephrines
• Imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computerized tomography (CT) scan, and ultrasound
These evaluations help determine if tumors are present on the thyroid, parathyroid, or adrenal glands and guide treatment planning.
Treatment
Treatment for MEN 2 focuses on managing tumors and preventing complications. Common conditions and treatments include:
• Medullary thyroid cancer: Surgical removal of the thyroid gland and surrounding lymph nodes is standard. Medicines may be used if the cancer has spread and cannot be surgically removed.
• Parathyroid enlargement: Surgery is typically used to remove all or part of the affected parathyroid glands while preserving healthy glands.
• Adrenal tumors: Depending on findings from imaging tests, one or both adrenal glands may need to be surgically removed.
Treatment plans are tailored to reduce symptoms, manage hormone imbalances, and prevent complications such as cancer or excessive hormone production. Regular follow-up care is important to monitor for new tumors or changes in existing ones.
Advertisement