Overview
Symptoms
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) may cause noticeable symptoms, though some people do not feel any changes in their heart rhythm. When symptoms are present, they can vary in intensity and frequency.
Common symptoms of atrial fibrillation include:
-
A fast, fluttering, or pounding heartbeat, often described as palpitations
-
Chest pain or discomfort
-
Dizziness or a feeling of unsteadiness
-
Fatigue or low energy levels
-
Light-headedness
-
Reduced ability to exercise or perform physical activities
-
Shortness of breath
-
General weakness
In some cases, atrial fibrillation causes no symptoms and is discovered during a routine health checkup.
AFib can occur in different patterns:
-
Occasional, also known as paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Symptoms start suddenly and stop on their own. Episodes may last from a few minutes to several hours or, in some cases, up to a week. The irregular heartbeat can return repeatedly.
-
Persistent atrial fibrillation. The irregular heart rhythm does not stop on its own and usually requires medical treatment to restore a normal rhythm.
-
Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. This form lasts longer than 12 months and often requires medications or procedures to manage the heart rhythm.
-
Permanent atrial fibrillation. The irregular rhythm cannot be restored to normal. Treatment focuses on controlling the heart rate and reducing the risk of blood clots and stroke.
If symptoms such as chest pain occur, immediate medical attention is required, as this may indicate a heart attack.
Causes
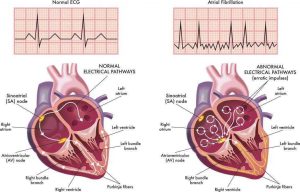
Atrial fibrillation occurs when the electrical signals that control the heart’s rhythm become disorganized. These faulty signals cause the upper chambers of the heart, called the atria, to beat rapidly and irregularly instead of in a steady, coordinated pattern.
Common causes and contributing factors of atrial fibrillation include:
-
High blood pressure that is not well controlled
-
Coronary artery disease or a history of heart attack
-
Heart valve problems
-
Congenital heart defects present at birth
-
Heart failure or weakened heart muscle
-
Previous heart surgery
-
Overactive thyroid gland
-
Lung diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
-
Sleep apnea
-
Excessive alcohol use, especially binge drinking
-
Use of stimulants, including certain medications
-
Severe infections or physical stress
In some people, atrial fibrillation develops without an identifiable cause. This is sometimes referred to as lone atrial fibrillation. Even when symptoms are mild or absent, atrial fibrillation can still increase the risk of serious complications such as stroke and heart failure, making proper medical evaluation and management important.
Advertisement