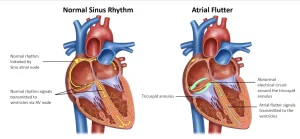
Atrial flutter is a type of abnormal heart rhythm known as an arrhythmia. It affects the heart’s upper chambers, called the atria, causing them to beat faster than normal. Atrial flutter is closely related to atrial fibrillation, but the electrical activity in atrial flutter is more regular and organized. Some people may experience both conditions at different times.
This condition may be discovered during a routine health check, especially if no symptoms are present. When symptoms do occur, they can affect daily activities and overall heart health. Treatment options often include medications and, in some cases, procedures to restore or control the heart rhythm.
Symptoms
Many people with atrial flutter do not notice any symptoms, and the condition may be found incidentally. When symptoms are present, they may include:
-
A rapid, pounding, or fluttering sensation in the chest
-
Chest discomfort or pain
-
Shortness of breath, especially during activity
-
Feeling unusually tired or weak
-
Fainting or feeling close to fainting
Causes
Atrial flutter is caused by changes in the heart’s electrical system. These changes interfere with how electrical signals move through the atria, leading to a fast but typically organized rhythm.
Certain medical conditions or heart-related procedures can alter normal electrical pathways. Damage to heart tissue, stress on the heart, or scarring from surgery may all contribute to the development of atrial flutter.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing atrial flutter. These include:
-
Heart failure or other structural heart problems
-
Chronic lung disease such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
-
A history of blood clots in the lungs
-
Congenital heart defects present from birth
-
Increasing age
-
Recent heart surgery or invasive heart procedures
Complications
Atrial flutter can lead to serious health problems if not properly managed. One common complication is atrial fibrillation, which develops in many people with atrial flutter over time. Atrial fibrillation significantly increases the risk of blood clots and stroke.
Other possible complications include:
-
Heart failure due to prolonged rapid heart rate
-
Stroke related to blood clot formation
-
Increased risk of heart attack