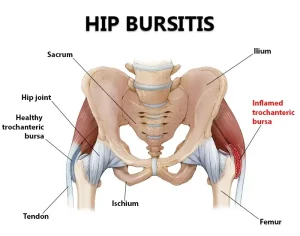
Overview
Bursitis is a condition caused by inflammation of a bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that cushions bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. Bursae help reduce friction during movement. When a bursa becomes irritated or inflamed, it can lead to pain and restricted movement. Bursitis most commonly affects the shoulders, elbows, hips, knees, and heels and can be acute or chronic.
Symptoms
Symptoms of bursitis depend on the affected joint and severity of inflammation. Common symptoms include:
-
Localized pain that worsens with movement or pressure
-
Swelling and tenderness around the joint
-
Stiffness or reduced range of motion
-
Warmth or redness over the affected area
-
Pain that increases after activity or repetitive use
In some cases, pain may develop gradually rather than suddenly.
Causes
Bursitis usually develops due to repeated irritation or pressure on a joint. Common causes include:
-
Repetitive movements or overuse of a joint
-
Prolonged pressure on one area, such as kneeling or leaning on elbows
-
Injury or trauma to a joint
-
Infections affecting the bursa
-
Underlying conditions such as arthritis or gout
Improper posture or poor body mechanics can also contribute.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing bursitis:
-
Repetitive physical activities or manual labor
-
Aging, as bursae become less resilient over time
-
Poor posture or joint alignment
-
Certain medical conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes
-
Occupations or hobbies involving frequent kneeling, lifting, or reaching
Complications
Most cases of bursitis improve with appropriate care, but complications can occur:
-
Chronic bursitis with recurring pain
-
Reduced joint mobility
-
Infection of the bursa, known as septic bursitis
-
Muscle weakness due to limited movement
-
Persistent discomfort affecting daily activities
Early treatment reduces the likelihood of long-term problems.
Prevention
Bursitis may not always be preventable, but certain measures can lower the risk:
-
Avoiding repetitive strain and taking regular breaks
-
Using proper techniques and posture during activities
-
Wearing protective padding for joints when needed
-
Maintaining flexibility and strength through regular exercise
-
Addressing joint pain early before it worsens
Good joint care and activity modification play an important role in preventing bursitis and maintaining mobility.
Advertisement