Overview
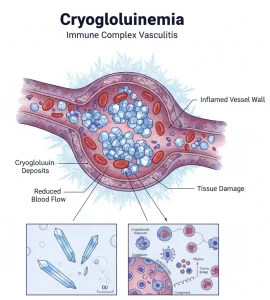
Cryoglobulinemia is a condition in which abnormal proteins in the blood, called cryoglobulins, become solid or gel-like at low temperatures. These proteins can block blood vessels and cause inflammation, leading to reduced blood flow to the skin, joints, nerves, and organs. Cryoglobulinemia is often associated with chronic infections, autoimmune diseases, or certain blood cancers. The condition can range from mild to severe, depending on the organs involved.
Symptoms
Symptoms of cryoglobulinemia vary widely and are often triggered or worsened by cold exposure.
Common symptoms include:
-
Purple or red skin spots, especially on the legs
-
Joint pain and stiffness
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
-
Skin ulcers or sores
-
Cold sensitivity in fingers and toes
-
Abdominal pain or kidney-related symptoms in severe cases
Symptoms may appear gradually or occur in episodes.
Causes
Cryoglobulinemia occurs due to the presence of cryoglobulins in the blood, which form in response to underlying conditions.
Common causes include:
-
Chronic hepatitis C infection
-
Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
-
Blood cancers, including multiple myeloma and lymphoma
-
Other chronic infections
-
Idiopathic cases where no clear cause is identified
The condition develops when cryoglobulins trigger inflammation in blood vessels.
Risk factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing cryoglobulinemia.
Risk factors include:
-
Chronic viral infections, especially hepatitis C
-
Autoimmune disorders
-
Blood or bone marrow cancers
-
Middle age or older adulthood
-
Female sex
Not everyone with these risk factors will develop the condition.
Complications
Untreated cryoglobulinemia can lead to serious organ damage.
Possible complications include:
-
Vasculitis causing tissue damage
-
Chronic kidney disease or kidney failure
-
Nerve damage leading to persistent numbness or pain
-
Skin ulcers with risk of infection
-
Gastrointestinal bleeding in severe cases
Early diagnosis and management help reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Prevention
Prevention of cryoglobulinemia focuses on managing underlying conditions and reducing triggers.
Preventive measures include:
-
Early treatment of hepatitis C and other chronic infections
-
Regular monitoring for autoimmune or blood disorders
-
Avoiding prolonged cold exposure
-
Following prescribed treatment plans
-
Routine medical follow-up to detect organ involvement early
Addressing the underlying cause is key to preventing disease progression and complications.
Advertisement