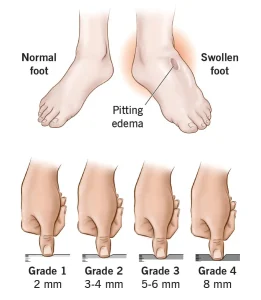
Overview
Edema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the body’s tissues, leading to swelling. It most commonly affects the feet, ankles, legs, hands, and arms, but it can occur in any part of the body. Edema may be temporary or chronic and can result from a wide range of medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle factors. Identifying the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of edema is visible swelling, which may develop gradually or suddenly. Common symptoms include:
-
Swelling of the legs, ankles, feet, hands, or face
-
Stretched, shiny, or tight-looking skin
-
Skin that retains an indentation when pressed
-
Heaviness or tightness in the affected area
-
Reduced flexibility or movement of joints
-
Discomfort or pain in severe cases
Causes
Edema occurs when fluid leaks from small blood vessels into surrounding tissues or when fluid removal is impaired. Common causes include:
-
Prolonged sitting or standing
-
High salt intake
-
Pregnancy
-
Injury or inflammation
-
Heart failure, kidney disease, or liver disease
-
Venous insufficiency or blood clots
-
Certain medications, such as blood pressure drugs or steroids
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing edema include:
-
Advanced age
-
Chronic heart, kidney, or liver disease
-
Obesity
-
Pregnancy
-
Sedentary lifestyle or limited mobility
-
Use of medications known to cause fluid retention
Complications
If edema persists or is left untreated, it may lead to several complications, depending on the cause and severity. Possible complications include:
-
Skin breakdown and infections
-
Reduced blood circulation
-
Pain and difficulty walking
-
Delayed wound healing
-
Increased risk of blood clots
-
Permanent tissue damage in chronic cases
Prevention
While not all cases of edema can be prevented, certain measures may help reduce risk and severity:
-
Maintaining regular physical activity and movement
-
Limiting salt intake
-
Elevating affected limbs when resting
-
Wearing compression garments if recommended
-
Managing underlying medical conditions
-
Following prescribed medication instructions
Early evaluation and treatment of edema can help prevent complications and improve comfort and quality of life.
Advertisement